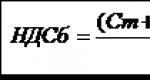Impact on the ruble exchange rate. Why is the ruble so unstable and what does the exchange rate in Russia depend on? The dollar as a world currency
With a high degree of probability, it can be argued that the most important of all factors influencing the dollar on the ruble is the price of oil in the world. As you know, Russia is one of the largest oil producers in the world, respectively, the economy is very driven by this factor, and it turns out that oil is the most basic raw material in Russia. From all this it follows that if oil quotes are rapidly going up (the price of petroleum products in dollars), then the dollar exchange rate against the ruble becomes lower. In general, this is the main external factor of the dollar's influence on Russia.
In the case when oil prices go down, this has a very detrimental effect on the Russian economy and currency, since in this case Russia begins to incur huge losses and, as a result, the ruble is devalued, and this is done so that the profit from oil products for Russia does not decrease , it turns out that at this moment the dollar begins to grow rapidly against the Russian ruble.
Plus, one of the significant external factors is the dollar exchange rate against other world currencies. Let's take as an example currency pair euro dollar, if the dollar begins to fall against the euro, then, in most cases, the dollar also begins to fall against the ruble, this happens in most cases.
Here we discussed the influence of external factors, now we come to the analysis of internal ones. The most important of all factors (internal) influencing the quotes of the Russian ruble is how much this currency is needed in Russia, that is, the ruble is in great demand in Russia or people prefer other currencies, since keeping money in these currencies in their opinion more stable.
Here is a very vivid example for you: the ruble begins to decline, and very clearly, then, in turn, all enterprises try to transfer their money, which in turn is in shares, into a currency that is more resistant to the vagaries of the market - the dollar, of course, it happens that money is transferred and into completely different currencies, but in most cases, the choice of people falls on the dollar, since this is the most common currency in the world, and no matter what they say, it is much more stable than other currencies. It also happens vice versa, when the ruble starts to rise in price, then it is natural that the demand for the ruble starts to rise just as much, in general, I would call these actions a kind of vicious circle.
Above, I listed the most basic aspects of the influence of the dollar on Russia, there are a huge variety of different kinds of influences, but less strong, for example, what is the trade turnover between Russia and America, it is also very important that if America supplies more goods to Russia than Russia to America , then this has a very detrimental effect on the ruble quotes, now I will explain why.
The thing is that Russia needs to pay for American goods directly in dollars, it turns out that Russia needs to exchange a large number of rubles into dollars, with the risk of losing money, since currency quotes jump all the time, and I'm not just talking about ordinary goods, and if we take, for example, aircraft, cruisers, any minerals on an industrial scale - after all, this is all a lot of money, and a change in the exchange rate by at least 1/10 of the ruble can lead to a huge loss of money and, as a result, a decrease in Russian ruble quotes.
But for Russia at the moment it is very good that if the dollar falls against other currencies, mainly against the euro, then against the ruble it starts to fall in much the same way. And this happens quite often, Russia is also affected by the amount of currency that is brought in and located on the territory of Russia, since many stores and enterprises are converted to dollars, and not only customers can count with any enterprises in dollars, many enterprises they specifically exchange and keep their capital in dollars, the Russian economy suffers greatly from this.
In my opinion, every effort should be made to ensure that the entire population in Russia, or most of it, would begin to trust the ruble no less than the dollar and try to use rubles in all calculations, this would greatly change the situation on the market, since The Russian ruble, I am more than sure under such circumstances, would begin to grow rapidly, subsequently the economy would begin to grow, and of course the standard of living, as I said, everything is quite closely interconnected, but it is only in words it is easy to do this, in reality everything much more difficult than it might seem at first glance.
Since, to face the truth, the dollar all over the world is a very significant currency that has gained great prestige, and it deservedly has the title of the most popular and most common currency, perhaps over the years something will change and the ruble will be trusted in the same way, like the dollar, but for now we need to be realistic and look at things correctly.
History of ruble crises in charts:
The summer vacation season that has come to an end is considered a kind of "marker" for the foreign exchange market. It is known that tourists mostly leave Russia, so vacationers increase the demand for dollars and euros, which should have a negative impact on the ruble exchange rate. "Lenta.ru" talked to foreign exchange market analysts to understand how seasonal factors are related to prices for dollars and euros.
Despite their impact on exchange rates, seasonal or cyclical, the causes of fluctuations are more likely to be the so-called second-order factors. They are able to provide temporary support to the ruble, but they are not able to form a serious trend. And, before talking about them, it is worth recalling the primary factors that affect the exchange rate.
Why the ruble depends on oil
The first fundamental factor that affects the exchange rate is the trade balance (the difference between the value of exports from a country and imports into it). So, Russian companies sell oil, gas and other raw materials mainly for dollars and euros, but in Russia they pay taxes and salaries to their employees in rubles.
Since oil and gas make up a significant part of Russian exports and are the source of almost half of the income state budget, they are considered the most important factor affecting foreign exchange earnings. Obviously, the amount of foreign exchange earnings depends on the cost of oil. Thus, the low cost of raw materials resulted in a significant devaluation of the ruble at the end of 2008.
In this regard, a reasonable question arises: why did the ruble not strengthen so much in 2012 (at the beginning of the year, the US dollar was trading at a price of 31.2 rubles, and on September 14 it cost 30.65 rubles), although oil held at a record level ? Here it is worth remembering another factor: the outflow of capital. In the first six months of this year, 42.4 billion dollars came from Russia. There are several reasons for this state of affairs, the main of which are a poor investment climate, political instability and corruption (dishonest officials are trying to withdraw money abroad and buy up foreign currency).
The exchange rate of the national currency is also influenced by numerous indicators that indicate the state of the country's economy: performance data, business activity index, information about housing construction, volumes of retail sales. The value of money is strongly influenced by speculation, as well as the expectations of companies and the public about the growth or fall of rates. Dmitry Kharlampiev from Petrocommerce Bank recalls that during the crisis period of 2008-2009, the share of deposits individuals in foreign currency increased from 13.5 percent to 34 percent. Thus, additional domestic demand for foreign currency amounted to about $40 billion, which put pressure on the ruble exchange rate.
The exchange rate of the national currency is also influenced by politics Central Bank. The Central Bank conducts foreign exchange interventions: it sells dollars and euros to support the ruble exchange rate, and buys up foreign currency when it does not want the national money to strengthen excessively. Another tool is the refinancing rate. If the Bank of Russia raises the rate, then the cost of borrowings for commercial financial institutions in the country grows. Consequently, the profitability of funds in Russia is increasing, and investors are sending more money to the Russian economy, and this spurs the demand for rubles. In addition, by raising the refinancing rate, the Central Bank reduces the issue of money, this reduces the supply of the ruble and, as a result, raises its value.
Finally, an increase in the refinancing rate reduces inflation, which is also a factor in the value of a currency. The higher the rise in prices, the faster the national currency becomes cheaper and the more its exchange rate falls. Of course, inflation is affected not only by the Central Bank's refinancing rate. For example, food inflation caused by drought can spur price growth and collapse the ruble exchange rate. Of the general economic factors, unemployment and GDP can also be distinguished: a decrease in the first and an increase in the second raises the exchange rate of the national currency.
Obviously, most of these factors are not able to instantly affect the change in the exchange rate. So, for example, the increase in the supply of the ruble after the reduction of the Central Bank rate will be gradual, and therefore its exchange rate should fall slowly. However, international investors, traders and many market participants who know that they will need foreign currency after some time (and it is better to buy it at a lower price), "win back" economic news immediately. For example, on September 14, after news from the United States about keeping the discount rate at a minimum and new injections into the economy, the dollar against the ruble immediately forty kopecks.
Second order factors
The above factors are considered the main ones. In turn, the reasons that can be called seasonal or cyclical are considered by most analysts to be secondary. In their opinion, they can fluctuate the exchange rate for some time, but seasonal factors are not capable of forming a certain trend, in contrast to the same reduction in the refinancing rate. Experts interviewed by Lentoy.ru estimate the change in the ruble exchange rate under the influence of cyclical factors at 0.5-1.5 percent, but no more.
One of these factors is the New Year holidays, when citizens start buying more goods supplied by importers, which sharply raises the demand for the currency and weakens the ruble. However, according to Anton Startsev, a leading analyst at IF OLMA, it is impossible to speak of a statistically significant confirmation of this trend. He cites the following statistics: for the period from 2002 to 2011 inclusive, the depreciation of the ruble against the US dollar in December was recorded in six cases out of ten. The average weakening was 1.2 percent. Startsev notes that if the crisis year of 2008 is excluded from the statistics (then there was a large-scale devaluation of the ruble), then it will look even less convincing.
In addition, by the end of the year, the ruble exchange rate is negatively affected by the fact that it is in the fourth quarter that a significant part of the budget is being used. Spending from the state treasury dramatically increases the amount of ruble liquidity in the economy. Dmitry Glubokovsky, an analyst at Aton Management, notes that some of these funds are used in the interests of individual businessmen (in other words, we are talking about corruption), who then withdraw money abroad. This, in turn, spurs the demand for foreign currency and puts a lot of pressure on the ruble.
However, at the end of the year, another seasonal factor has an impact - the end of the reporting period and the payment of taxes. Russian companies. This increases the demand for ruble liquidity, which has a positive effect on the ruble exchange rate. According to Startsev, this trend is noticeable at the end of each month, but to a greater extent - at the end of the quarter.
"On the whole, only the tax period is the most predictable and regular event, which makes it possible to unequivocally assess the likelihood of a possible strengthening of the ruble," notes Alexei Egorov, an analyst at Nomos-bank. He names another factor: the period of payment of dividends by Russian companies. Since a number of their owners are not residents, they convert the received money into foreign currency, which temporarily lowers the ruble exchange rate.
In addition, the demand for foreign currency is spurred by payments on foreign debts. According to Deputy General Director for investment analysis IC "Zerich Capital Management" Andrey Vernikov, in recent years, the peak of these payments falls on September and March - therefore, the demand for currency during this period is high. He notes that a liquidity shortage usually forms by the middle of the year, which also spurs demand for foreign currency.
As for the vacation period and the possible pressure on the ruble associated with it, analysts do not consider it to be a significant reason. Firstly, this period is too spread out: the holiday season starts in May and lasts until September, and besides, many people go abroad both in autumn and in winter. Secondly, within the framework Russian economy in general, spending by tourists is not very significant. But experts agree that, in general, the trade balance (and hence the exchange rate of the ruble), any sector of the economy in which Russia is a net importer, including tourism, is negatively affected.
Thus, other things being equal, we can say that the national currency can grow at the end of each month, and especially strongly at the end of the quarter. Expect it to go down in price new year holidays, as well as news about the payment of dividends. However, due to the large number of mutually influencing and mutually intersecting factors, "ideal conditions" should not be expected.
A few months ago, oil suddenly began to become cheaper, the dollar and euro rates first crept, and a little later they jumped up, making our ruble cheap, and this was the beginning of a crisis from which Russia has not yet emerged. A cheap ruble is beneficial for the state, but not for ordinary citizens. Let's see what determines the exchange rate of the ruble against the dollar and the euro. It is no less interesting to know whether it is possible to predict a rise in price or a fall in price of the Russian currency.
Educational program for dummies
We will try to briefly and in simple words conduct an educational program, as they say, for dummies, about how Russian ruble becomes more expensive and cheaper.
Price movements on currency exchanges only seem chaotic, in fact, the value of the ruble, dollar and euro depends on a number of circumstances that are quite man-made.
Related articles:
It is possible to divide the factors on which the price of a currency in Russia depends on external and internal.
We list the reasons that externally affect the exchange rate of the ruble against the dollar:
- World oil prices- In Russia, almost everything depends on the sale of oil today. Being in fact a raw materials appendage of the civilized world, our country is directly dependent on oil trades, and since the price per barrel is set in dollars, the higher it is, the higher the price of the ruble against the dollar.
Related video:
But when oil prices fall, there is a loss of profits in Russia and the devaluation of the ruble immediately follows to avoid a decrease in the ruble equivalent of revenue from oil sold.
- The value of the dollar against the currencies of other countries- if the US dollar falls in price, for example, against the euro, its price also decreases against the ruble.
Now let's look at the internal factors on which the dollar/ruble exchange rate in Russia depends:
- Demand for foreign currency– fluctuations in the value of securities on stock market lead to an increase in demand for a stable currency, that is, for the US dollar. And along with demand, the price of the dollar rises. In order to prevent the situation from developing into a crisis, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation conducts foreign exchange interventions, knocking down the excessively increased dollar exchange rate.
- Political and economic situation in Russia- the value of domestic money largely depends on the mood in the society and its trust in the authorities. In crises, the population starts to buy dollars and euros, believing that, in this way, they will protect their savings from loss, thereby provoking an increase in the price of foreign currencies and bringing down the value of the ruble.
Do not hurry!
In our review, it is important for a teapot to understand one thing: you should not immediately succumb to the whipped up hysteria and run to the exchanger to buy dollars and euros, trying to get rid of the cheaper rubles. The ongoing crisis is largely to blame for those same currency speculators who artificially inflated the price of the dollar in the wake of panicky rumors about cheaper oil.
Someone got rich dramatically, and the vast majority of the population of Russia had to tighten their belts, being broke, with a suddenly cheaper salary, with which you can buy less and less.
What can affect the dollar exchange rate and how, what factors put pressure on the US currency and what the USDRUB quote depends on. You will learn about the internal and external factors that form the USD price below.
The dollar exchange rate is of interest to any financier in any country of the world, because it is this currency that has the greatest impact on world economy, as well as on the dynamics of other monetary units. The position of the dollar is changeable, and in order to correctly predict its movement and get the opportunity to make money on it, you need to know the factors of influence that determine the value of the American currency.
The main impact on the dollar exchange rate on international market traditionally rendered, as well as the monetary policy pursued by the American regulator - Fed(Federal Reserve System, FED). At the same time, the dollar, along with the euro, is the world's leading reserve currency, and a large number of countries that keep part of their foreign exchange reserves in American currency are oriented towards its exchange rate. This status of the USD does not provide for a sudden rise in price or reduction in price and is a sign of the high stability of its exchange rate.
Changes in the Fed's monetary policy are always closely related to the economic situation in the States.
For example, strong macro reports increase the risk that monetary policy will be tightened.
Also, such news increases investment attractiveness country. At the same time, both of these factors strengthen the dollar in the foreign exchange market.
The release of negative data on macroeconomics causes a backlash. For example, on October 15, 2014, US retail sales figures came out, which turned out to be weaker than analysts' forecasts: the indicator fell by 0.3% against expectations of 0.1%. The news provoked powerful fall US currency against competitors, as forecasts for tightening the monetary policy of the US regulator were lowered.
Formation of the dollar exchange rate in market conditions
The American dollar is the “world currency”, the rate of which is oriented to the vast majority of countries in the world. The process of forming its course is based on foreign economic activity: the agents present in the system of the economy, who are engaged in settlements with foreigners, simultaneously form both the demand and supply of the national currency in the market.
To put it simply, supply/demand is created by only two sides..
- Importers. They buy foreign goods for dollars and sell them domestically for the national currency. That is, these are agents of demand for the dollar, which give their own currency for the American one for making purchases abroad.
- Exporters. They sell goods abroad for dollars, and inside the country they buy for the national currency or invest in their production. Exporters are supply agents who convert foreign dollar earnings into their own currency.
Accordingly, the demand for the currency grows with an increase in the volume of imports, and the supply - with growing exports. The difference between incoming and outgoing financial flows reflects one of the most important macroeconomic indicators for the dollar, called the trade balance. This indicator may be deficient ( below zero) and surplus ( above zero). Thus, a compromise price is established, at which importers agree to buy American currency, and exporters agree to sell.
Based on the described mechanism, we can formulate the basic rule for the formation of the exchange rate: the currency becomes more expensive when the trade balance increases and becomes cheaper when it decreases. At the same time, it is not the actual (absolute) indicators that are considered important, but the dynamics itself. For example, if the balance in the previous year was -8, and for the current year it was set at -6, then this indicates a positive trend, that is, the depreciation of the currency will slow down. And if the trade balance was +9 and became +7, then, despite the surplus, the dollar may start to fall.
Factors influencing the dollar exchange rate
Events that can influence the position of the dollar in the market can be divided into two large groups.
- Domestic political and economic factors of the issuing state - the United States.
- Events in the outside world that put pressure on the formation of the US dollar.
Internal events
TO internal factors and reasons for the fluctuation in the value of the USD include all important economic and financial news in the United States. In addition, every policy measure that may affect the country's economy must be taken into account.
The factors influencing the dynamics of the currency include the exit economic indicators(indicators, indices). Naturally, not every published indicator will lead to a sharp jump in the rate, but some stand out among them, which are of particular importance and have a strong influence on quotes. They deserve the attention of every market participant.
The list of important indicators includes the following:
- Gross Domestic Product Growth Rate Data - GDP(Gross Domestic Product, GDP) USA. This indicator reflects general position of the country's economy, its increase indicates an increase in production and the service sector. An increasing GDP growth rate strengthens the currency, while a falling one weakens it.
- Index of industrial(Producer Price Index, PPI) and consumer prices (Consumer Price Index, CPI).
- Rising/falling unemployment(change in the number of employees, Nonfarm Payroll). Traders do not consider this indicator in absolute terms, but trace the relativity with previous values. An increase in the number of unemployed indicates a deterioration in the economy and leads to a fall in the value of the USD.
- country's balance of payments(Balance of Payments).
- Import/Export Level. The growing volume of imports indicates a decline in the national economy (the production level is declining, unemployment is growing), which has Negative influence to the exchange rate. With an increase in exports, the situation changes in the opposite direction. As a rule, this indicator is published as the difference between imports and exports (Balance of Trade).
- New home sales(New Home Sales). An increase in housing sales indicates an increase in the purchasing power of Americans, as well as the fact that their housing problems are being solved and they will continue to purchase other goods, which stimulates production growth. Increasing real estate purchases are strengthening the USD.
- Durable Goods Orders(Durable Goods Orders). The market is actively responding to this indicator, because it allows you to make a forecast about the future dynamics of the activity of the manufacturing sector.
- Oil reserves according to the US Department of Energy(EIA Crude Oil Stocks). The indicator reflects the level of reserves in the country's fuel sector. It has a significant impact not only on the USD exchange rate, but also on the oil market.
- Chicago Fed National PMI(Chicago Fed National Activity Index). The essence of the index is that it is the main barometer of the American economy, therefore it strongly affects the fluctuations in the value of the dollar.
- Index consumer prices (Consumer price index, CPI). The indicator is calculated once a month and reflects the country's inflation rate. It refers to very important indicators, so the market reacts sensitively to its publication.
Another reason for changes in the exchange rate of the dollar are financial factors that characterize the situation in the sector of intrastate banking services. Significant among these indicators are:
- The degree of stability and reliability of the work of organizations specializing in financial services.
- The volume of money supply (Quantity of Money).
- Level key rate(Interest Rate), percent securities and others.
- The degree of inflation (monitored using the consumer price index, industrial prices).
- Level credit rate(Federal Funds Rate). Decreasing this parameter increases purchasing power population, but, on the other hand, causes an increase in the money supply, which weakens the dollar. Data on the rate are announced by the governors of the US National Bank.
The value of the USD is also affected by the policies pursued by the US government. This is due to the fact that any politician has his own special view of the economy, based on which he prepares a program for its development. Therefore, with a change of power, the economic situation often changes very profoundly, which is reflected in the position of the US dollar on the world stage.
In addition, the US currency, like any other, can be affected by events that have no direct connection with either politics or finance.
Such factors include any natural disasters, natural disasters (floods, fires, earthquakes, hurricanes, wars, terrorist attacks, etc.). For example, the market reacted to the news about the tragedy of September 11, 2001 in New York with a large-scale collapse of the dollar against major currencies.
The internal factor influencing the USD rate, which is the most important, is the Fed discount rate. An increase in its level leads to the strengthening of the American currency, a decrease - to a weakening.
External events
External factors are events that affect the value of the dollar that occur outside the United States. The most critical of the external factors is the level of confidence in the currency. The impact of investor confidence is hard to overestimate: its lack may well lead to a collapse of the existing exchange rate, it is enough for one of the largest market participants to refuse to use the dollar as monetary unit for international payments.
Moreover, Iraq and Norway have already done this when they began to use the euro when paying for oil.
Another significant factor in pressure on USD quotes are and . The reason for this is the fact that the United States is one of the world's largest consumers of oil. The increase in the cost of this energy carrier entails a steady decline in the dollar. With regard to gold, a similar situation can be observed.
Significant pressure on the exchange rate is exerted by the participation of the United States in various armed conflicts ( Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria) regardless of the results. Man-made disasters and natural disasters outside the United States are also negative factors influencing the USD exchange rate.
What determines the exchange rate of the dollar to the ruble
The exchange rate is called its value as a commodity in the real economy, and first of all it depends on the balance of supply and demand for currency markets. Fluctuations in the dollar (), like any other convertible currency, depend on many circumstances, which include internal and external factors. Among the main factors of influence are the decisions of the Central Banks and the monetary policy of the respective international organizations concerning the currency they issue.
To understand what determines the dollar exchange rate in Russia, it is necessary to answer two main questions.
- How does the policy of the country's regulator affect the exchange rate, pushing it in certain directions that differ from the market balance?
- How is the formation of the dollar exchange rate in market conditions?
Let's consider the questions in order.
The influence of the regulator on the exchange rate
The main goal of each central bank is to contain the devaluation of the national currency. This position is justified by the fact that if the dollar becomes expensive inside a country, then imported goods also become more expensive, which negatively affects the standard of living of citizens.
 World Central Banks, including the National Bank of Russia, have at their disposal a fairly rich arsenal of restrictions that apply to the market rate. Here are the main ones:
World Central Banks, including the National Bank of Russia, have at their disposal a fairly rich arsenal of restrictions that apply to the market rate. Here are the main ones:
- Applying a fixed rate. This measure is dangerous for the economy due to the fact that the gold and foreign exchange reserves of the state are spent on holding the value of money. At the same time, the population of the country is not informed about the real market rate.
- Establishing a price band. To prevent sharp exchange rate fluctuations, as well as panic tendencies, the regulator sets the upper and lower limits (corridor) of permissible fluctuations. For example, using a corridor with a width of 4%, the Central Bank prohibits the sale of the dollar by more than 4% above or below the average market rate for the current day.
- Currency interventions. central bank he himself acts as a buyer of currency in the market, replenishing the gold and foreign exchange reserve. At the same time, he plays to increase the rate. He can also act as a major seller, which holds back the devaluation of the national currency.
- Key rate setting(percentage of lending to commercial banks by the central bank). An increase in the rate strengthens the ruble, as it increases the number of people who want to keep their savings in rubles. This is due to the fact that the profitability of bank deposits depends on it.
Market factors influencing the dollar exchange rate in the Russian Federation
citizens Russian Federation American dollars are traditionally treated with confidence because of their low inflation. However, it should be understood that the dollar is a freely convertible currency, so at some points it is subject to significant fluctuations.
The value of the dollar in Russia largely depends on the market exchange rate of the ruble. Factors influencing the RUB can be divided into two groups: strengthening and weakening. The main circumstance related to the first group is the growth in the cost of crude oil on the world market. This is due to the fact that the profit from the sales of black gold makes up the bulk of the budget of the Russian Federation. Therefore, each jump in the price of this energy carrier has a positive effect on the value of the ruble, lowering the quotes of the USD\RUR pair.
Ruble strengthening factors also include:
- confidence in the national currency on the part of enterprises and the population;
- increase in domestic production, entailing a reduction in imports;
- stable political environment;
- foreign investment in the Russian economy.
The group of phenomena negative for the ruble exchange rate includes:
- falling oil prices;
- panic among the population, provoking a massive buying of dollars and euros;
- decline in national production, accompanied by an increase in imports (stagnation of the economy);
- refusal of the National Bank of the Russian Federation to carry out dollar interventions;
- falling GDP growth;
- Western sanctions against Russia;
- exchange speculations of large market players;
- buying up foreign currencies with its further transfer to offshore.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
What affects the dollar exchange rate? After all, it is the US currency that is the main exchange commodity presented in many markets. And there are many reasons for such popularity, among which is the relative instability (volatility) of its course.
In order to predict other currencies, you should know the main reasons and factors that affect how demand and supply for this currency will be formed.
What affects the dollar exchange rate? Reasons and factors affecting the value of the US currency
The dollar exchange rate changes regularly, which makes it possible, with the right choice of the direction of the transaction, to make pretty good money.
But for the correct choice of this direction, it is necessary to clearly understand what causes and factors most influence the fact that the trend of the dollar against various currencies, including the ruble, is constantly changing. It is the consideration of such factors that allows you to make for maximum income.
Today, there are two main groups of those factors that have the main influence on the formation of a trend in the US currency:
- the first includes events occurring directly within the state,
- and the second group is formed from external factors that somehow put pressure on the formation of the value of the national currency.
So, what influences the dollar exchange rate from the inside, that is, what internal government reasons and factors put pressure on the formation of the value of the dollar. These factors can be attributed absolutely, which relate to financial sphere and the economic condition of the United States. In addition, it is necessary to take into account political changes that affect the economic spectrum in one way or another.
Do economic data influence how the dollar exchange rate changes?
The next factor influencing the process of forming the dollar exchange rate is publications.

At the same time, it should be taken into account that not all indices can cause sharp changes in the exchange rate of the US currency, so you need to pay attention only to the most significant of them.
These indices include:
- industrial and consumer price index,
- the rate of inflation and unemployment,
- balance of payments indicator
- and some other indicators of macroeconomics.
The influence of financial factors - as another reason for the dollar exchange rate fluctuations
The dollar exchange rate is also influenced by financial factors that characterize the state of the banking services sector within the state as a whole.
These factors include:
- the stability of the functioning of institutions providing financial services,
- as well as changes in indicators of the volume of money supply,
- discount rate, interest on securities, and so on.
Political factors, no matter how strange it may seem, are also capable of shaping the dollar. Well, this is due to the fact that each of the politicians has his own program for the development of the economy, and his coming to power sometimes radically changes economic situation in the country. The reasons and factors influencing the dollar exchange rate may also be of a different nature, not related to politics and finance (at least not directly).

For example, it can be all kinds of natural disasters and disasters (earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, etc.). Also, do not discount reports of terrorist attacks - remember what a collapse of the dollar was observed after the events in New York on September 11, 2001.
The main indicator that affects the exchange rate fluctuations of the dollar today
And finally, the most important indicator on which the dollar exchange rate depends is the discount rate of the US Federal Reserve. If this rate increases, then the dollar exchange rate increases accordingly, and, conversely, if it decreases, the price of the US currency will decrease.
What affects the dollar exchange rate within the state, we have considered, now let's see what causes and factors put pressure on the US currency from the outside. These factors include events that take place outside the country of the issuer, but in one way or another affect the value of its national currency.
What external causes and factors affect the dollar exchange rate?
The main external factor is confidence in the currency. This factor is capable of literally collapsing the existing exchange rate, for this it will be enough for one of the major market participants to declare their refusal to use the US dollar as an international settlement currency.You don't have to look far for a clear example - Norway and Iraq did this in their time, switching to the euro when paying for oil.
Also, one of the fundamental external factors that shape the dollar's exchange rate is the price of gold and crude oil.For the simple reason that the United States is one of the largest consumers of oil in the world, it inevitably leads to the depreciation of their currency. Exactly the same dependence is observed during changes in the value of gold.

What affects the exchange rate of the dollar against the euro?
The most important of the factors of key importance in the influence of the dollar against the euro is the US monetary policy.
The instruments of such a policy used by the Central Bank of the country are:
- open market operations (operations conducted on the open market);
- the discount rate (regulation of the discount rate);
- reserve requirements (change the levels of reserve requirements).
The discount rate and reserve requirements are handled by the Fed, while open market operations are controlled by the Federal Committee of that market. The use of these instruments has a strong impact on the amount of funds held by depository institutions in the accounts of the Federal reserve bank, which leads to a change interest rates mainly by short-term loans and causes exchange rate fluctuations.
The monetary policy of the Eurozone, which also affects the exchange rate of $ against the euro, is determined by the European central bank (European Central Bank).
The main goal of this policy is to ensure and maintain price stability based on price events in the future, and is defined as an increase in the Harmonized Consumer Price Index.
Another aspect of price stability is monetary growth with a target level set by the ECB of 4.5% annually. In addition, a 3-month Eurodeposit "EURIBOR" - placement of deposits in banks located outside the EU zone, as well as 10-year Government Obligations, which are the differences between the Eurozone and the USA, have a 3-month Eurodeposit "EURIBOR" on the dollar against the euro.
What affects the dollar against the ruble?
In Russia, they also monitor changes in exchange rates and are interested in what reasons and factors have the most significant impact on the attitude. There are two groups of factors that influence the national currency in Russia - those that contribute to strengthening and that have a negative impact.
To the first group of factors One of the factors that contribute to the strengthening of the ruble, of course, is the increase in world prices for crude oil, since the profit received from its sales is one of the main parts of the state budget. For this reason, any fluctuation towards an increase in the cost of oil will have a positive effect on the ruble exchange rate.
This group of factors includes:
- confidence of enterprises and the population in the ruble,
- increasing domestic production and gradually reducing imports,
- investing in the country's economy of non-resident capital,
- and a stable political environment.
The second group of factors negatively affecting the ruble exchange rate includes:
- the panic of the population,
- massively buying euros and dollars,
- stagnation of the economy (lack of own production and an increase in imports),
- the absence of dollar interventions by the Central Bank,
- slowdown in GDP growth,
- as well as the purchase of currency (dollars, euros), which will later be transferred to offshore zones.
All this undoubtedly has the most significant impact on the dollar against the ruble.
Exchange rates and their trends on the stock exchange. Reasons for their hesitation