Test "Unemployment, types and forms of unemployment." Social studies test on the topic "employment and unemployment" Economic problems of unemployment test
Short description
1. Unemployment caused by constant changes in the allocation of society's resources between types and spheres of production of goods and services:
a) frictional b) voluntary c) hidden d) cyclic e) forced
2. Unemployment caused by major structural changes in the economy, when society gets rid of outdated enterprises, sub-sectors, sometimes even entire industries, which entails the disappearance of a large number of jobs for those who worked there before:
a) seasonal b) voluntary c) hidden d) forced e) Structural
Attached files: 1 file
Test on the topic "Unemployment"
1. Unemployment caused by constant changes in the allocation of society's resources between types and spheres of production of goods and services:
a) friction
b) voluntary
c) hidden
d) cyclical
d) forced
2. Unemployment caused by major structural changes in the economy, when society gets rid of outdated enterprises, sub-sectors, sometimes even entire industries, which entails the disappearance of a large number of jobs for those who worked there before:
a) seasonal
b) voluntary
c) hidden
d) forced
e) Structural
3. Unemployment, which reflects the number of unemployed citizens looking for work, ready to start work and registered with the state employment service:
a) hidden
b) registered
c) seasonal
d) temporary
e) social
4. What kind of unemployment refers to workers employed in production, but in reality being “superfluous”:
a) indirect
b) straight
c) open
d) hidden
e) temporary
5. Unemployment, which is generated by the temporary nature of the performance of certain types of activities and the functioning of economic sectors:
a) friction
b) temporary
c) seasonal
d) structural
e) cyclical
6. What problem is unemployment?
a) macroeconomic
b) microeconomic
c) biological
d) extensive
e) indirect
7. A phenomenon organically related to the labor market:
a) trade
b) addiction
c) unemployment
d) employment
d) unemployment
8. The unemployed are:
a) part of the working-age population that remains after deducting the employed;
b) able-bodied individuals who do not work
c) part of the economically active but unemployed population, which remains behind
d) deducting persons who do not intend to work and therefore are not looking for work;
e) part of the economically active population that remains after deducting the employed;
9. The level at which full employment of the labor force is ensured, i.e. its most effective and rational use:
a) indirect
b) natural
c) natural
d) natural
d) hidden
10. Psychological and social and political consequences of job loss:
a) macroeconomic consequences of unemployment
b) economic consequences of unemployment
c) non-economic consequences of unemployment
d) psychological consequences of unemployment
d) there is no correct answer
11. The unemployment rate refers to the percentage of the country’s population that is older:
12. The consequence of insufficient volumes of total expenditures of the population causes:
a) regional unemployment
b) seasonal unemployment
c) frictional unemployment
d) structural unemployment
d) cyclical unemployment
13. If the actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate by 1%, the lag of actual GDP from potential is 2-2.5%. this is the law:
b) Okena
c) Nobel
d) Herman
d) Lenin
14. Labor supply, like labor demand, depends on the level of:
a) companion
b) employees
c) working conditions
d) wages
e) enterprises
15. Employment reflects ... labor supply and labor demand:
a) merger
b) ratio
c) compliance
d) responsibility
Unified State Exam tests "Unemployment"
1. Are the following statements about labor force and unemployment true?
A. The number of employed and the working-age population always coincides.
B. Unemployment excludes able-bodied people who have not reached retirement age from social production.
2. In country A. coal has ceased to be used in the energy industry. Most of the mines closed and miners lost their jobs. What type of unemployment is observed in country A?
1) natural 3) friction
2) structural 4) seasonal
3. Are the following judgments true about the conditions conducive to reducing unemployment?
A. Conditions that can influence a decrease in the unemployment rate include an increase in unemployment benefits.
B. Conditions that can influence the reduction in unemployment include a reduction in taxes on producers.
4. Cyclical unemployment has the lowest rates in conditions
1) decline in industrial production
2) peak of the financial crisis
3) revival and recovery in the economy
4) long recession
5.
A. Unemployment is a natural consequence of market regulation of the economy.
B. Each country has its own level of unemployment, unchanged for many decades.
1) only A is true 3) both judgments are true
2) only B is true 4) both judgments are incorrect
6. One of the directions of state policy in the field of employment is
1) updating human resources through youth employment
2) employment of the population at state enterprises
3) financing of employment of the population in private enterprises
4) promoting the growth of structural unemployment
7. Are the following statements about unemployment true?
A. An unemployed person is any person who does not work.
B. Unemployment increases during an economic crisis.
1) only A is true 3) both judgments are true
2) only B is true 4) both judgments are incorrect
8. Cyclical unemployment is at its highest.
1) at the peak of economic activity
2) at the lowest point of the decline in economic activity
3) during a period of growth in economic activity
4) during a period of stable economic development
9. In the list below, circle those categories of the population that are included in the labor force, and circle the numbers under which they are listed.
1)
housewives,
2) part-time workers,
3) those who do not have a job, but are actively looking for one,
4) those serving a sentence in prisons,
5) working on a flexible schedule.
10. The growth of unemployment in traditional industries and the availability of vacant jobs in the high technology sector characterizes the situation on the market
1) capital 3) labor
2) goods and services 4) securities
11. Due to the downturn in global financial markets, a large investment bank has reduced the number of its branches and some of its staff. The above example illustrates unemployment
1) frictional 2) seasonal
3) cyclical 4) structural
12. A woman on maternity leave belongs to the category
1) employed in social production
2) structural unemployed
3) permanently disabled
4) not included in the workforce
13. A person who is sick with bronchitis and for this reason is temporarily unable to work belongs to the category:
1) busy
2) unemployed
3) temporarily unemployed
4) not included in the total workforce
14. Non-economic negative consequences of unemployment include
1) increased competition in the labor market
3) lost production
2) slowdown in wage growth
4) increase in the number of offenses
15. In country A., during the economic crisis, many citizens lost their jobs. They cannot find it for a long time and rely on temporary, odd jobs. Select characteristics of unemployment in country A from the list below and write down the numbers under which they are listed.
friction 4) cyclic
seasonal 5) hidden
open 6) structural
16. Are the following statements about unemployment correct?
A. The unemployed include all people of working age who do not have a job.
B. Unemployment is inherent in all economic systems.
1) only A is true 3) both A and B are true
2) only B is true 4) both judgments are incorrect
17. Establish a correspondence between the forms of unemployment and specific examples that illustrate them.
|
EXAMPLES |
FORMS OF UNEMPLOYMENT |
|
A) After a significant part of the residents left the village for the capital, the local bakery closed due to lack of orders, workers lost their jobs. |
|
|
B) After harvesting the citrus fruits, the workers received a payment. |
1) structural |
|
C) The production of the plant was declared unprofitable, the workers were fired. |
2) cyclic |
|
D) In the conditions of the financial crisis, the company reduced the number of teams to service the mine. |
3) seasonal |
|
E) A hotel employee lost his job in the fall after the departure of the last group of tourists. |
18. Establish a correspondence between the types of unemployment and the corresponding citizens who have lost their jobs.
|
Citizens |
Types of unemployment |
|
A) a nurse who quit because of an allergy to medications |
|
|
B) a bank employee dismissed due to the liquidation of a branch caused by the financial crisis |
1) friction 2) cyclic |
|
C) a worker at an automobile plant who was fired due to a reduction in car production caused by unfavorable economic conditions |
|
|
D) a qualified lawyer who left the firm due to a conflict with management |
|
|
D) a manager of an enterprise who quit due to moving to another city. |
19. Select examples from the list below that illustrate the manifestation of frictional unemployment in the labor market:
1) Citizen M., a qualified economist, did not work for two years while caring for her sick mother, having started looking for work, she could not find a place in her specialty, refusing
go to work as a courier.
2) Due to a long recession, the company was forced to lay off about a third of its staff, and put some employees on indefinite leave without pay.
3) Due to the ban on gambling, all city casinos were closed, and their staff lost their jobs; former croupiers need to retrain.
4) A pediatrician moved for family reasons to another city until he could find a job in his specialty and receives unemployment benefits.
5) Due to the economic recession in the country, many bank and office employees, “office plankton”, lost their jobs
6) A former banking lawyer with work experience is looking for a job in his field; the vacancies offered to him did not suit him because the salary was too low.
20. Find examples of cyclical unemployment in the list below and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) With the advent of computers, secretaries-typists were not in demand in the labor market.
2) The economic crisis has led to an increase in unemployment at enterprises in various industries.
3) Employees of an enterprise that went bankrupt in conditions of intense competition lost their jobs.
4) With a decrease in orders at the stage of economic recession, the construction company began laying off employees.
5) With the completion of the fruit harvest in the horticultural farm, seasonal workers received their pay and went home.
Report on teaching practice
Completed by: Baidosova Kristina Aleksandrovna
Group MGMU-12
Teacher: Rezer Tatyana Mikhailovna,
Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences, Professor
Ekaterinburg 2013
Project topic"Unemployment"
Pedagogical goal
1) To increase the theoretical level of students’ knowledge of economics;
2) Develop the ability to make comparisons, analyze, draw conclusions, rationally solve cognitive and problematic problems, reveal the most important theoretical principles and concepts using examples, participate in discussions, and engage in research activities;
3) Form an attitude towards the problems of unemployment;
4) Promote the development of cognitive activity, the formation of information and communication culture of students.
Target For students development of economic culture
Tasks For teacher
1) Define unemployment and analyze the differences in the causes of each type of unemployment;
2) Give a formula for calculating the unemployment rate;
3) Give examples of all types of unemployment;
4) Get acquainted with the features of unemployment in Russia
Tasks For students
Learn to calculate the unemployment rate
Be able to analyze information and draw your own conclusions
Equipment:
Lesson type: combined
Textbook:
Chernyak V.Z. Economy. Tables and diagrams. M., 2009
Determine the form of the lesson (lecture, seminar, business game, round table, etc.)
Words that students will learn in class:
Unemployment, types of unemployment: frictional, structural, hidden, full employment, unemployment rate, economically active population, natural rate of unemployment, economic and social consequences of unemployment, unemployed, able-bodied citizens.
RELEVANCE OF THE TOPIC:
Unemployment is a macroeconomic problem that has the most direct and severe impact on people. Losing a job for most people means a decline in their standard of living and causes psychological trauma. Therefore, many politicians use the so-called “poverty index” to generally assess the state of the economy, which is the sum of unemployment and inflation rates as two main indicators of macroeconomic instability.
Economists study unemployment to determine its causes and to develop better social employment programs.
The concept and essence of unemployment.
Work on the formulation of the concept, writing in a notebook: Unemployment– This is a socio-economic condition in which part of the economically active working population cannot find work that these people are capable of performing.
Causes of unemployment.
Work on the text of the manual, identifying the causes of unemployment.
· Structural changes in the economy.
· Economic recession or depression.
· Government and trade union policies in the field of remuneration.
· Seasonal changes in the level of production in certain sectors of the economy.
· Changes in the demographic structure of the population.
Conversation on the issue " Unemployment in Russia, in the Russian Federation." Students work in groups, asking questions to each other.
Conclusions of the conversation: For Russia, unemployment is a relatively new phenomenon. The average unemployment rate in Russia is beyond the threshold of 10%. The official unemployment rate in Russia is small, but the actual scale and level are much higher. At the beginning of 2011 in Russia, taking into account hidden unemployment, its actual level reached more than 20%. The number of economically active population of the Russian Federation aged 15-72 years (employed + unemployed) in February 2012. amounted to 74.7 million people, or about 53% of the total population of the country.
Anticipatory task " Unemployment level in the Artinsky district."
As of October 1, 2012, the level of registered unemployment in the Artinsky district was 0.86, the level of general unemployment was 7.0%. On average, there are 3 vacancies per unemployed citizen who applies to the employment service, but the average salary for announced vacancies is 39% lower than the average salary in the region (10.9 thousand rubles versus 17.9 thousand rubles) of the total number of vacancies, the share of vacancies with pay below the subsistence level is 24.7%. The most in demand in the region's labor market are construction workers, drivers, gas-electric welders, machine operators, and medical workers. It is important to note that about 10 thousand people of the working population work outside the region, mainly in the city of Yekaterinberg.
Filling out the table “Types of employment”.
Unemployment is frictional- this is temporary unemployment caused by the voluntary transition of an employee from one job to another, which causes the period of temporary dismissal
Unemployment is structural- unemployment caused by changes in the structure of demand and production technology. Such changes lead to the need to develop new professions, and workers who do not possess these professions are released and forced to retrain.
Technological unemployment- unemployment associated with mechanization and automation of production, as a result of which part of the workforce becomes redundant or requires a higher level of qualifications.
Unemployment is institutional- unemployment that occurs when the state or trade unions intervene in establishing wage rates different from those that could be formed in a natural market economy.
Unemployment is cyclical- this is the inability to find work in regions and countries affected by economic recession, when even the total number of available jobs is less than the number of unemployed.
Hidden unemployment- typical for the domestic economy; its essence is that the company does not fire workers, but transfers them either to reduced working hours (part-time work week or working day), or sends them on forced unpaid leave.
Unemployment is voluntary- This is unemployment associated with the reluctance to work in conditions of reduced wages.
Unemployment is stagnant- a type of unemployment in which workers are faced with the inability to find work due to the fact that the region in which they live is affected by an economic crisis.
Unemployment is seasonal- Occurs regularly at certain times of the year. It is especially typical for agriculture, where after harvesting there is a break in work due to purely weather climatic conditions.
Tasks to consolidate what has been learned (intermediate control)
Student assignment No. 1.
Write down the word missing from the table:
Answer: structural
Student assignment No. 2.
Citizens of the country of India have been unable to find work in their specialty for a long time, because the demand for labor has changed: a number of professions have become outdated and become unclaimed. Long-term unemployment alternates with short periods of temporary, casual work. Select characteristics of unemployment in the country of India from the list below and write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1. Seasonal 4. Structural
2. Hidden 5. Friction
3. Stagnant 6. Open
Answer: 3; 4; 6
Subtopic: “Measuring the unemployment rate”
Students listen to the explanation and analyze the graph.
The main indicators that measure unemployment are the so-called unemployment rate and the average duration of unemployment. The unemployment rate is determined by the formula:
Table: “Labor force:
· Economically active population: employed and unemployed
Economically inactive population (voluntarily unemployed)
Students listen to the explanation and take notes.
If the actual unemployment rate exceeds its natural rate, the country loses part of its GDP. The calculation of potential losses of products and services as a result of rising unemployment is carried out on the basis of a law formulated by an American economist Arthur Oaken.
If the actual unemployment rate is 1% higher than the natural one, then the actual output will be lower than the potential one by b% (Ouken's economically determined parameters). According to Okun's calculations, in the 1960s. in the USA, when the natural rate of unemployment was 4%, the parameter b was equal to 3%.
Okun's Law states that when the actual unemployment rate increases by 1% above its natural level, actual GDP decreases compared to the potential (at full employment) GDP by an average of 3%.
Solving problems to consolidate a subtopic:
Student assignment No. 3.
Are the following statements true about conditions that can affect the reduction in unemployment?
A. Conditions that can affect the reduction in unemployment include an increase in unemployment benefits
B. Conditions that can affect the reduction in unemployment include a reduction in taxes
1. Only B is true 3. Both judgments are true
2. Only A is correct 4. Both judgments are incorrect
Entry in the notebook “Social consequences of unemployment”:
1) negative
· Aggravation of the crime situation
Increased social tension
Increase in the number of physical and mental illnesses
Increased social differentiation
· Decrease in labor activity
2) positive
· Increasing the social value of the workplace
· Increased personal free time
· Increased freedom to choose where to work
· Increased social significance and value of work
Student assignment No. 4.
Highlight the negative consequences of unemployment. Answer:
· Underutilization of the economic potential of society, when real GNP is significantly less than potential
Decline in the standard of living of the population
· Those who lose their jobs receive only unemployment benefits
· Consumer demand is declining
· Incomes of employees are decreasing
· Loss of professional knowledge and skills
· Psychological trauma leading to alcoholism, drug addiction, suicide, and increased crime.
Student assignment No. 5.
Write down the word missing in the diagram.

Answer: unemployed
Student assignment No. 6.
Read the text below, each position indicated by a specific letter.
(A) The International Labor Organization counted 210 million unemployed people in the world in 2010. (B) This is nothing more than a manifestation of the economic crisis. (B) The number of unemployed people increased by more than 30 million. (D) Many experts believe that the historical maximum in global unemployment has not yet been passed.
Student assignment No. 7
Explain how you understand this parable: "Unemployed Angel"
There were two angels. One simply sat idle, and the other was constantly at work - either he would descend to Earth, or he would rise to Heaven. And this is how it is at work all the time.
The unemployed angel decided to ask another:
Why are you constantly flying back and forth?
I carry messages to God that begin with the words “Lord help...”, said the working angel, “why aren’t you doing anything?”
I must carry messages to the Lord that begin: “Thank you, Lord...”.
III. Lesson summary:
Consolidation of the studied material. Review questions:
1. What is unemployment?
2. What are the main types of unemployment?
3. How do you understand the term “full employment”?
4. What is the unemployment rate?
5. What are the economic and social consequences of unemployment?
Work in groups (solving tests).
1. Are the following statements true?
A. Unemployment leads to income redistribution.
B. If the unemployment rate decreases, this always means that more people of working age have jobs.
a) only A is true; c) both statements are correct
b) only B is true; d) both judgments are incorrect.
2 . Are the following statements true?
A. The main reason for frictional unemployment is imperfect information.
B. Sectoral shifts in the economy can lead to an increase in frictional unemployment.
a) only A is true; c) both statements are correct
b) only B is true; d) both judgments are incorrect
3. In economic theory, full employment is usually understood as a situation where there is no unemployment:
a) cyclical; b) frictional c) structural
4. The unemployment rate is calculated as a percentage of:
a) non-working people to the number of working people;
b) unemployed to the size of the labor force;
c) unemployed to the working-age population;
d) unemployed to the labor force.
5. The economically active population is:
a) unemployed people looking for work;
b) pensioners;
c) employed people.
6. Frictional unemployment occurs in the case of:
a) low population mobility;
b) lack of labor market;
c) demographic decline;
d) the emergence of some professions and the disappearance of others.
7. Structural unemployment occurs in the case of:
a) economic recession;
b) imbalances in supply and demand in the labor market;
c) changes in the place of residence of employees;
8. Cyclical unemployment occurs in the case of:
a) a crisis in the country’s commodity markets;
b) changes in the place of residence of employees;
c) the seasonal nature of the activity;
d) imperfections of labor legislation.
Reflection. Filling out the student's self-control sheet.

Control questions
Used Books
additional literature
Lesson equipment: multimedia equipment, presentation "Unemployment", course textbooks:
· Lipsits I.V. Economy. Moscow, Vita - Press, 2008,
· Lyubimov L.L.; Ranneva N.A. Fundamentals of economic knowledge. M.: Vita - Press, 2000,
· "Russian Economy", supplement to the textbook "Applied Economics" Junior Achievement, M, 1998,
· Savitskaya E.V. "Economics lessons at school" Moscow, Vita - Press, 2004,
· Rom V.Ya., Dronov V.P., Geography of Russia. Population and economy. 9th grade, Moscow, Bustard, 2008
· Alekseev A.I., Nikolina V.V., Geography. Population and economy of Russia. 9th grade, Moscow, Education, 200
Fill out the table
PROJECT NAME
| Indicators | Content | Type of training | Methods and means of teaching | Forms of control |
| Subject | Unemployment | Combined lesson Conversation, problem solving | group work, collective, individual, frontal. | testing |
| Teacher's goal | To increase students’ theoretical level of knowledge in economics; | |||
| Learner's goal | ||||
| Teacher's tasks | 1) introduce students to one of the main problems of the economy - unemployment , to generate knowledge about unemployment, its causes, types and consequences. 2) Form an attitude towards the problems of unemployment; | |||
| Student tasks | Develop the ability to make comparisons, analyze, draw conclusions, rationally solve cognitive and problematic problems, reveal the most important theoretical principles and concepts using examples, participate in discussions, and engage in research activities; | |||
| Project form | ||||
| Implementation method | ||||
| Planned result |
Lesson objectives:
· Educational –
· Developmental –
· Educational –
· Educational: introduce students to one of the main problems of the economy - unemployment , to generate knowledge about unemployment, its causes, types and consequences.
· Developmental: show the situation on the labor market in general and in modern Russia, develop economic thinking through information analysis, development of skills in comparison and analysis, working with statistical data, diagrams and maps.
· Educating: to develop communicative competence through work in groups, responsibility for economic decisions, respect for work, use of acquired knowledge when choosing a profession and orientation in the labor market.
Lesson objectives:
Educational:
· students’ understanding of the question of which people are classified as unemployed.
· show students that there are different forms of unemployment;
explain how they differ from each other.
· Consider the features of unemployment in Russia at the present stage.
Developmental:
· Economic thinking, economic literacy, economic skills, etc.
· Ability to pose economic problems.
· Ability to defend your point of view and show determination in various activities.
Educating:
· Culture of communication, mutual respect.
· See the economic side of the surrounding reality.
· Ability to adequately fit into the situation on the labor market.
· Lesson objectives:
· 1) Increase students’ theoretical level of knowledge in economics;
· 2) Develop the ability to make comparisons, analyze, draw conclusions, rationally solve cognitive and problematic problems, reveal the most important theoretical principles and concepts using examples, participate in discussions, and engage in research activities;
· 3) Form an attitude towards the problems of unemployment;
· 4) Promote the development of cognitive activity, the formation of information and communication culture of students.
Lesson objectives:
· Educational – consider the types and causes of unemployment. Become familiar with the concept of “full employment.” Teach students to calculate the unemployment rate.
· Developmental – comprehension of already known knowledge about unemployment, the ability to analyze the information received and draw your own conclusions.
· Educational – development of economic culture of students.
· Lesson objectives:
1) Define unemployment and analyze the differences in the causes of each type of unemployment;
· 2) Give a formula for calculating the unemployment rate;
· 3) Give examples of all types of unemployment;
4) Get acquainted with the features of unemployment in Russia.
The purpose of the lesson: introduce students to the phenomenon of unemployment.
Lesson delivery forms:
· lecture with elements of lively and dynamic dialogue with students.
1. Equipment: diagrams, tables, diagrams, package of documents.
2. Lesson type: combined
3. Textbook: Lipsits I.V. Economy. Basic course. Textbook for grades 10, 11. M., 2012
4. Chernyak V.Z. Economy. Tables and diagrams. M., 2009
Plan for learning new material
I. Unemployment is a companion of a market economy.
II. Causes of unemployment. Types and forms of unemployment.
III. Economic and social consequences of unemployment.
IV. The role of the state in providing employment.
1. Plan.
1. The concept of unemployment. Signs of being unemployed.
2. Unemployment rate, employment rate.
3. Causes of unemployment.
4. Solving the problem.
5. Types of unemployment:
· Frictional unemployment.
· Structural unemployment.
· Cyclical unemployment.
6. Consequences of unemployment.
7. State policy to combat unemployment.
8. Performance of search groups.
Lesson type: mastering new knowledge using ICT technologies
Lesson methods: partially search, analytical, heuristic, explanatory and illustrative.
Forms of work: group work, collective, individual, frontal.
Means of education: presentation for the lesson, “Dictionary of terms and concepts in social studies,” notebooks, handouts.
Software: Microsoft Office Power Point, Microsoft Office Word, Internet websites.
Equipment: computer science room (PC according to the number of working groups, projector, screen).
Test "Unemployment, types and forms of unemployment."
1. The following are considered unemployed:
1) the entire non-working population;
2) those who want to work, but are unable to get a job that matches their professional qualifications;
3) unemployed and receiving unemployment benefits;
4) those who have lost the ability to work.
2. The form of manifestation of natural unemployment is:
1) friction;
2) voluntary;
3) hidden;
4) cyclical.
3. Those who lost their jobs due to the crisis (recession) in the economy are classified as unemployment:
1) structural;
2) cyclic;
3) friction;
4) seasonal.
4. Those who have lost their jobs due to the introduction of new equipment and technology into production are classified as unemployment:
1) structural;
2) cyclic;
3) friction;
4) seasonal
5) the correct answer was not entered.
5. Those who lost their jobs due to changes in the structure of the economy are classified as unemployment:
1) cyclic;
2) friction;
3) seasonal;
4) the correct answer was not entered.
6.What is the name of the type of unemployment associated with searching and waiting for work?
1) structural;
2) seasonal;
3) friction;
4) cyclical.
7. Types of unemployment.
| Type of unemployment | Causes |
Worksheet for the lesson
1. If the unemployment rate does not change, then the number of people employed must equal the number
A. Unemployed.
B. Lost jobs.
C. Job seekers.
D. Those who left the workforce.
Answer: B. The number of people leaving jobs must equal the number of people employed for the unemployment rate to be constant.
See Section 5-1.
2. If the employment rate increases, then the natural rate of unemployment will be
A. Remain constant.
B. Increase.
C. Decrease.
D. Increase or decrease depending on the level of layoffs.
Answer: C. As explained in Section 5-1, the higher the employment rate, the lower the natural rate of unemployment.
3. Suppose that every month 2% of the employed lose their jobs (s = 0.02) and 38% of the unemployed find work (f = 0.38). Then the sustainable unemployment rate is
Answer: B. As explained in Section 5-1, the steady-state unemployment rate
4. Unemployment rate - 10%. The layoff rate is 5%. What should the employment rate be to keep the unemployment rate constant?
Answer: B. Since 90% of the total workforce is employed and the layoff rate is 5%, 4.5% of the workforce loses their jobs in each period. For unemployment to be constant, the same proportion of the labor force must find work in each period. See Section 5-1.
5. Unemployment insurance mainly increases
A. Frictional unemployment.
B. Seasonal unemployment.
C. Teenage unemployment.
D. Cyclical unemployment.
Answer: A. Because unemployment insurance programs reduce associated economic hardship, they increase frictional unemployment. See Section 5-2.
6. Unemployment caused by the fact that it takes time to match workers and jobs is called
A. Frictional unemployment.
B. The effect of "desperate" workers.
C. Unemployment waiting.
D. Wage rigidity.
Answer: A. For a discussion of frictional unemployment, see Section 5-2.
7. Frictional unemployment occurs because
A. The minimum wage is too high.
B. Unions exert pressure on the labor market.
C. There is rigidity in the salary setting process.
D. It takes time to establish a match between firms.
and employees.
Answer: D For a discussion of frictional unemployment, see Section 5-2.
8. What policies will reduce frictional unemployment?
A. Reducing corporate taxes.
B. Increase unemployment insurance.
C. Increase in the minimum wage.
D. Community retraining programs.
Answer: D. Public retraining programs facilitate the transition of workers from "declining" to "growing" industries, thereby reducing frictional unemployment. See Section 5-2.
9. If the government increases unemployment insurance, then we can expect that the rate of frictional unemployment
A. Will go down.
B. Will remain constant.
C. Will increase.
D. First it will increase, then it will decrease.
Answer: C. If unemployment insurance increases, the economic hardship of unemployed workers decreases, thereby reducing the incentive to look for work. This increases frictional unemployment.
See Section 5-2.
10. If real wages are above the equilibrium level, then labor supply
A. Depends on the nominal salary.
B. Less demand for labor.
C. Equal to labor demand.
D. greater demand for labor.
Answer: D. If the real wage is above the equilibrium value, then the supply of labor is greater than the demand for labor. See Section 5-3.
11. Unemployment caused by wage rigidity and lack of jobs is called
A. Natural rate of unemployment.
B. The effect of "desperate" workers.
C. Unemployment waiting.
D. Conflict between insiders and outsiders.
Answer: C. For a discussion of unemployment waiting, see Section 5-3.
12. A teenager cannot find a job because the acceptable minimum wage is higher than the salary that the company can offer him.
This situation is an example
A. Frictional unemployment.
B. Unemployment waiting.
C. Cyclical unemployment.
D. Effective unemployment.
Answer: B For a discussion of unemployment waiting, see Section 5-3.
13. Minimum wage laws - example
A. Collective agreement.
B. Wage rigidity.
C. The effect of "desperate" workers.
D. Insiders and outsiders.
Answer: B. Minimum wage laws prevent nominal wages from falling below a certain level. Thus, they determine the rigidity of wages. See Section 5-3.
14. Waiting unemployment occurs when
A. It is known that the minimum wage will increase by
in the nearest future.
B. Generous unemployment insurance was introduced.
C. Workers are temporarily laid off due to weather conditions.
D. Real wages are above the equilibrium level in the labor market.
Answer: D. For a discussion of waiting unemployment, see Section 5-3.
15. Which of the following does not determine real wage rigidity?
A. Minimum wage laws.
B. Unemployment insurance.
C. The power of unions.
D. Incentive salary.
Answer: B For a discussion of the reasons for real wage stickiness, see Section 5-3.
16. Unemployment caused by trade unions or the threat of unionization of workers - sample
A. Unemployment waiting.
B. The effect of "desperate" workers.
C. Incentive salary.
D. Conflict between insiders and outsiders.
Answer: D. Unemployment occurs because workers already hired
(insiders) fight to maintain high salaries. High wages keep the firm from hiring new workers (outsiders). See Section 5-3.
17. Unions can cause unemployment if
A. Outsiders contribute to lower wages.
B. Insiders maintain real wages above the equilibrium level.
C. Outsiders are subject to minimum wage laws.
D. Insiders are fired and outsiders are hired.
Answer: B. Unions can keep wages above their equilibrium level by causing the supply of labor to exceed the demand for labor. The resulting form of unemployment is called "waiting unemployment." See Section 5-3.
18. Efficiency wage theories argue that firms can pay high real wages in order to
A. Avoid the threat of workers unionizing.
B. Make work more productive.
C. Eliminate the use of unskilled workers.
D. Reduce the rate of frictional unemployment.
Answer: B. For an explanation of wage efficiency theories, see Section 5-3.
19. Incentive salary does not lead to
A. Unemployment waiting.
B. Setting wages above their equilibrium level.
C. A decrease in the firm's profits.
D. Increase worker productivity.
Answer: C. Firms pay incentive wages to increase worker productivity. This leads to increased profits for firms.
See Section 5-3.
20. Which of the following statements regarding unemployment is true?
A. Most periods of unemployment are long periods.
B. Most of the unemployed are long-term
unemployed.
C. The long-term unemployed make up only a small portion
unemployed.
D. Most of those who become unemployed remain
unemployed for a long time.
Answer: B. Most periods of unemployment are short-lived, but most unemployed people at any given time are in long-term periods of unemployment. See Section 5-4.
21. Compared to long-term unemployment, short-term unemployment is more likely to occur
A. Frictional unemployment.
B. Unemployment waiting.
C. A result of minimum wage laws.
D. The result of the actions of trade unions.
Answer: A. Short-term unemployment is more likely to be frictional unemployment. See Section 5-4.
22. Suppose that 130 people were unemployed for some part of a given year: 120 were unemployed for 1 month; 10 - unemployed for a year; What percentage of total months of unemployment is considered long-term unemployment?
Answer: D. There are 240 total months of unemployment, of which half is short-term unemployment and half is long-term unemployment. See Section 5-4.
23. Measured unemployment may be lower than actual unemployment because
A. Measured unemployment does not include frictional unemployment.
B. Some workers want to find a job but are desperate and
stopped searching for her.
C. Some who call themselves unemployed are simply not
They are seriously looking for a job.
D. Unemployment measured does not include teenage unemployment.
Answer: B. If workers who would like to work become discouraged and no longer look for work, actual unemployment will be higher than measured unemployment. See Section 5-4.
24. “Desperate” workers who would like to work, but have stopped looking for a job
A. They constitute frictional unemployment.
B. Constitute unemployment expectations.
C. No longer counted in the labor force.
D. Receive benefits in accordance with the legislation on
minimum wage.
Answer: C. That portion of the population that is not working or looking for work is considered to have dropped out of the labor force and is not counted in unemployment statistics. See Section 5-4.
TEST ON THE TOPIC: "EMPLOYMENT AND UNEMPLOYMENT"1. SELECTION OF ONE OR MORE CORRECT ANSWERS FROM THE PROPOSED LIST OF ANSWERS
1. Does not relate to the peculiarities of the labor market
1) sale of labor on the labor market
2) constant excess of labor demand over its supply
3) labor market regulation
4) variability of the labor market due to changes in the structure of professional training
2. Labor supply depends on
1) the share of the working-age population in its total number
2) migration opportunities of the population
3) length of the working day
4) all of the above
3. The most likely cause of unemployment is
1) structural changes in the economy, leading to the disappearance of outdated industries and the emergence of new ones
2) increase in the number of private (non-state) enterprises
3) increased competition between manufacturers
4) monopolization of certain sectors of the economy
2. IDENTIFYING STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF CONCEPTS USING CHARTS AND TABLES.
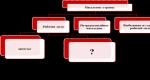
1. Write down the word missing in the diagram
Answer: ______________________________
2. Write down the word missing in the table
Types of unemployment | Causes of unemployment. |
characteristic of an economic crisis, resulting from a decline in production. |
|
Structural | impossibility of employment due to differences in the structure of demand and supply of labor of different qualifications. |
depends on work at certain times of the year (agricultural workers, guides). |
|
Friction | impossibility for a dismissed employee to find a free position in his specialty |
Answer: _________________ and ___________________________.
3. Write down the word missing in the table
Answer: ___________________________ .
3. ESTABLISHING THE CORRESPONDENCE OF POSITIONS PRESENTED IN TWO SETS.
1. Are the following judgments about the causes of structural unemployment true?
A. The cause of structural unemployment is the increase in demand for labor resources.
B. The cause of structural unemployment is the onset of a certain time of year.
2. Are the following statements about unemployment true?
A. An increase in unemployment reduces the demand for goods in the country's domestic market.
B. Unemployment is aggravating the political situation in the country.
1) only A is true 3) both judgments are true
2) only B is true 4) both judgments are incorrect
3. Establish a correspondence between the examples and types of unemployment: for which position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column.
Examples | Types of unemployment |
A. for certain professions there is a problem of employment at certain times of the year | 1. Temporary. |
B. Structural transformation of individual enterprises, job reductions. | 2.Seasonal |
B.transition from one place of work to another or initial job search. | 3.Structural |
D.Searching for and waiting to go to work | 4.Cyclic |
D. Cyclical market development determines the number of jobs | 5.Friction |
Write down the selected numbers in the table under the corresponding letters
4. DIFFERENTIATION IN SOCIAL INFORMATION OF FACTS AND OPINIONS.
1. Read the text below, each position of which is indicated by a specific letter.
(A) Unemployment is a macroeconomic problem. (B) It seems that full employment is nonsense and incompatible with the idea of a market economy. (B) Frictional and structural unemployment is, according to economists, completely inevitable. (D) The full employment unemployment rate is achieved when cyclical unemployment is zero.
1) factual nature
2) the nature of value judgments
2. Read the text below, each position of which is indicated by a specific letter.
(A) some researchers believe that the situation on the labor market directly depends on the demographic processes occurring in the country. (B) For 1993-2000. Russia's population decreased by 3.5 million people. (B) Moreover, the population decline is accompanied by its aging. (D) Thus, this will apparently lead to an increase in the average age of workers and a decrease in their labor mobility.
Determine which provisions of the text are
1) reflect the facts
2) express opinions
Write down in the table next to the letter indicating its character.
3. Below is a list of terms. All of them, with the exception of one, characterize the concept of “employment contract”. Find a term that “falls out” from the general series and write down the number under which it is indicated.
1) term 4) administrative punishment
2) test 5) labor discipline
3) rest time 6) dismissal
5. DEFINITION OF TERMS AND CONCEPTS CORRESPONDING TO THE PROPOSED CONTEXT.
1. In country N., the existence of unemployment is indicated by the presence of a high level of vacancies that cannot be filled without retraining workers. What type of unemployment occurs in country N?
1) cyclic 3) frictional
2) hidden 4) structural
2. Below are a number of characteristics related to the concept of “Labor Market”. Write down the characteristic that falls out of this series.
1) Unemployment rate 3) employment
2) wages 4) hyperinflation
5) structural unemployment
3. Read the text below, in which a number of words are missing. Select from the list provided the words that need to be inserted in place of the gaps.
In accordance with the Law on ______________ (A) of the population in the Russian Federation, the unemployed are those able-bodied _____________ (B), who do not have a job and ______________ (C), are registered with the employment service in order to find a suitable job, are looking for _____________ (D) and are ready to start her. At the same time, payments to _______________(D) and maintained average earnings to citizens, dismissal due to _______________(E) of an organization or termination of activities by an individual entrepreneur, reduction in the number or staff of employees of an organization, or individual entrepreneur are not taken into account as earnings.
The words in the list are given in the nominative case. Each word (phrase) can be used only once. choose one word after another, mentally filling in each gap. Please note that there are more words in the list than you will need to fill in the blanks.
List of terms:
1) employment 5) citizen
2) severance pay 6) liquidation
3) earnings 7) privatization
4) work
The table below shows the letters representing the missing words. Write down the number of the word you chose in the table under each letter.
6. FIND, CONSCIOUSLY PERCEIVE AND ACCURATELY REPRODUCE THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THE TEXT AND APPLY THEM IN THE GIVEN CONTEXT.
In Russia, the transition from full and unconditional employment in social production, corresponding to the universality and compulsory nature of labor under socialism, to a system of economic activity that meets the criteria of a market economy has taken place. More than half of the economically active population does not work for government agencies, but for themselves, working in enterprises and private-corporate organizations. At the same time, 15% are employed in small businesses. About 9% are classified according to the ILO methodology as unemployed...
The proportions of the distribution of employed people have changed in favor of those industries whose business activity has increased due to market transformations: trade and public catering, logistics and trade intermediation, lending, finance and insurance... In terms of the share of unemployed in the total economically active population, our country has almost caught up with the UK, Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden.
The visible metamorphoses of employment reflected changes in the nature and content of “direct social labor.” From collective forced activity for the production of planned products and services of a given quantity and range, labor becomes a way of existence for economically independent commodity producers. Public and collective labor is being replaced by private individual labor.
The revolution in property and the accompanying institutional transformations in the economy led to the fact that millions of people, previously engaged in systematically organized professional work for the state, tested their strengths and abilities in hitherto persecuted entrepreneurship and in small business, where labor, property and management are fused together ( control). Almost ¼ of those employed in the private sector are non-wage earners. Their activities combine professional and innovative work in very different proportions and, at the same time, management work with executive work.
(I. Zaslavsky)
1) What problems of the social and labor sphere of life in Russian society does the author highlight and consider?
2) Name the changes that have occurred in the content and nature of social labor, the position of the employee as a result of market transformations.
3) What does I. Zaslavsky mean when he states: “In Russia, the transition from full and unconditional employment in social production... to a system of economic activity that meets the criteria of a market economy has taken place”? Based on the text, find an explanation for this statement.
4) What changes have occurred in the sectoral structure of employment of Russians during the development of market relations in the economy? Based on your knowledge of the facts of social life, give examples that confirm these changes.
1. Comment : this task is aimed at identifying the awareness of perception and the accuracy of reproducing information contained in the text explicitly. The content of the correct answer and instructions for assessment suggest that the answer should indicate problems in the social and labor sphere of life in Russian society.
2. Comment : This task is aimed at transformative reproduction and interpretation of the text without the use of contextual knowledge. The content of the correct answer and instructions for assessment (other wording of the answer is allowed that does not distort its meaning).
3. A comment : this requires the use of additional material, it aims at characterizing the text or its individual provisions in connection with the course studied, at interpreting the content of the text based on one’s own knowledge. Contents of the correct answer and instructions for assessment (other wording of the answer is allowed that does not distort its meaning)
4. Comment : the task is aimed at using knowledge obtained from the text in another situation, one’s own argumentation and the formulation of value judgments regarding the positions stated in the text. Contents of the correct answer and instructions for assessment (other wording of the answer is allowed that does not distort its meaning)
7. INDEPENDENTLY DISCOVER THE MEANING OF KEY SOCIAL SCIENTIFIC CONCEPTS AND APPLY THEM IN THE GIVEN CONTEXT.
What meaning do social scientists give to the concept of “unemployment”. Using knowledge from a social science course, make two sentences: one sentence containing information about the types of unemployment, and one sentence revealing any function of unemployment.
A comment . The task involves defining a concept and composing two informative sentences with it, reflecting certain theoretical or factual social scientific data.
Let's consider an algorithm for performing tasks of this type.
When starting to complete the task, you need to understand the meaning of the requirements:
when reading the task, pay attention to what and in what quantity you need to name; do not provide more positions than required in the condition;
you need to double-check your answers, discarding questionable answer options.
Let's start completing the task by understanding the requirement. The first question (“What is the meaning of social scientists in the concept of “unemployment”?”) involves reproducing the definition of the concept of “unemployment” (the first element of the answer). The second task (Make two sentences using this concept in the context of social science knowledge) involves composing, based on social science knowledge, two sentences with one sentence containing information about the types of unemployment, the second, revealing any of the functions of unemployment (the second and third element of the answer). It must be emphasized that sentences must contain meaningful information, and it is not easy to mention this term. The main sentences must demonstrate
knowledge of social science course.
8. CONCRETE WITH EXAMPLES THE STUDYED THEORETICAL POSITIONS AND CONCEPTS OF SOCIAL SCIENCES FORMING THE SOCIAL SCIENCES COURSE.
Give two positive and two negative consequences of unemployment, illustrating each with a specific example.