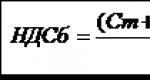The kbm for the specified data is 1.55. Problems of determining cbm (discounts for break-even OSAGO). From the history of KBM
Bonus-Malus Ratio (BMF)- coefficient of insurance rates depending on the presence or absence of insurance compensation carried out by insurers in the previous period, from April 1 of the previous year to March 31 inclusive of the year following it, when compulsory insurance civil liability of the owner vehicle.
Replacement of a driver's license (VL) and/or last name, first name and/or identity documentIf you have changed your driver's license and/or last name, first name and/or identity document, you must make changes to the current OSAGO agreement as soon as possible. This is necessary to enter the correct information into the automated information system of the Russian Union of Motor Insurers (AIS RSA) and assign the correct KBM in the future.
In accordance with paragraph 8 of article 15 federal law 40-FZ P: “During the validity of the OSAGO contract, the insured is obliged to immediately inform the Insurer in writing about changes in the information specified in the application for concluding an insurance contract.” In case of simultaneous validity of several OSAGO agreements, it is necessary to make changes to each of these OSAGO agreements.
You can write an application for changes. You can make changes to the electronic OSAGO policy through.
The procedure for determining the KBMFrom April 1, 2019, the CBM is calculated once a year - on April 1 and is applied throughout the entire period (from April 1 to March 31) for the conclusion of any contract.
The MSC coefficient of a driver who owns a vehicle - an individual, or a person authorized to drive a vehicle owned by an individual or entity, including cases when the compulsory insurance contract does not provide for limiting the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle (hereinafter referred to as the driver's KBM), in respect of which the CMTPL AIS contains information on compulsory insurance contracts, is determined based on the value of the KBM coefficient, which was determined by the driver for the MBM period, and the number of insurance claims under all compulsory insurance contracts carried out by insurers in respect of this driver and registered in the OSAGO AIS during the MBM period.
Policy with a limited list of drivers
General order
Under a compulsory insurance contract that provides for limiting the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle, the CBM is determined on the basis of information in relation to each driver. KBM is assigned to each driver who is allowed to drive the vehicle specified in the contract. When calculating the insurance premium, the highest value of the CBM coefficient is applied. In the absence of information about the insurance history, the driver is assigned KBM = 1.
- The insured, who is an inscribed Driver No. 1 with a BMF equal to 0.9, entered Driver No. 2 with a BMF equal to 1.4 into the OSAGO policy, since it was his fault that the insurance indemnity was paid to a contract that ended no more than a year ago. Accordingly, the size of the insurance premium will be determined by driver #2, and the premium will be increased due to the lower coefficient of driver #2.
- Driver #1 and driver #2 have the same BMR of 0.8. The insured entered driver No. 2 into the OSAGO policy. Accordingly, the fact of adding a second driver to the policy will not affect KBM under the contract, and the insurance premium will remain unchanged.
If the driver was not previously included in the OSAGO policy (for example, he just received a driver's license)
In the absence of information in the AIS RSA for the drivers specified in the contract, they are assigned KBM = 1.
- Driver #1 got his license and bought the vehicle two days later. When drawing up an OSAGO agreement, such a driver is assigned KBM = 1.
Policy without restrictions
For compulsory insurance contracts that do not provide for limiting the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle owned by individual, the insurance rate is calculated using the KBM coefficient equal to 1.
If the previous contract was terminated early
When concluding a new OSAGO agreement, the KBM will be equal to the KBM, which was determined on April 1 of the current year.
If an accident happened
If you were an injured party as a result of an accident, then the payment for this accident will not affect your accident class (ACC) in any way. If you are the culprit of the accident, then the CBM will be reduced only for the driver who was the culprit of the accident.
Break in insurance 1 year or more
In order to determine the cost of an OSAGO policy, various parameters of the KBM data table are taken into account. Some indicators are constant and unchanged, while others may change their value somewhat, which will determine the final cost of insurance.
One of these indicators is BMB (bonus-malus coefficient). And to calculate it, you can use a special calculator on the site.
What is KBM for?
For each car, and for each specific motorist, the final cost of OSAGO will be excellent. And all because both the power of the vehicle and the driving skills of a particular motorist are taken into account. And the younger the driver and he has less driving experience, the more expensive the insurance will be.
Each Insurance Company is primarily interested in attracting customers who have accident-free driving experience, that is, the absence of accidents, at least through the fault of their client. Such motorists bring the greatest profits to the company.
If to speak in simple words, then the malus bonus coefficient is a kind of discount for motorists for the fact that they drive carefully and do not get into an accident through their own fault.
And for each such year of accident-free driving, the motorist can expect to receive a larger percentage of the discount. There is a special KBM table that provides information on insurance discounts.
Coefficient calculation
Every year there are some updates to the data, so the 2018 OSAGO KBM table looks like this.
KBM OSAGO table
| Class | cbm | A discount | Class at the end of the insurance period, taking into account insured events for it | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 payouts | 1 payout | 2 payouts | 3 payouts | 4 payouts | |||
| M | 2,45 | + 145 % | 0 | M | M | M | M |
| 0 | 2,3 | + 130 % | 1 | M | M | M | M |
| 1 | 1,55 | + 55 % | 2 | M | M | M | M |
| 2 | 1,4 | + 40 % | 3 | 1 | M | M | M |
| 3 | 1 | no | 4 | 1 | M | M | M |
| 4 | 0,95 | — 5 % | 5 | 2 | 1 | M | M |
| 5 | 0,9 | — 10 % | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | M |
| 6 | 0,85 | — 15 % | 7 | 4 | 2 | M | M |
| 7 | 0,8 | — 20 % | 8 | 4 | 2 | M | M |
| 8 | 0,75 | — 25 % | 9 | 5 | 2 | M | M |
| 9 | 0,7 | — 30 % | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | M |
| 10 | 0,65 | — 35 % | 11 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 11 | 0,6 | — 40 % | 12 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 12 | 0,55 | — 45 % | 13 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 13 | 0,5 | — 50 % | 13 | 7 | 3 | 1 | M |
- The first column stands for the class of the driver in OSAGO at the time of insurance. A novice motorist who applied to the company for the first time receives the third class. And it is from him that the calculation will take place in the future, in the direction of decreasing or increasing.
- The second column contains information about the CBM for OSAGO, which corresponds to this class.
- The rest of the table is quite easy to decipher, it contains information about the classes that can be assigned depending on the presence or absence of insured events for this particular auto insurance period. That is, the column contains information about the number of motorist calls to the company during the insurance period.
Rules for using the table

Calculation of KBM according to the table has quite simple rules calculus. And in order to find out the KBM coefficient, you will need to have information about the initial value of the assigned class, as well as the number of insured events with the driver under the previous contract, if any.
The price of an insurance contract will depend on which class of CBM will be applied. Using data from a table is quite simple. To determine the coefficient, it is necessary to have information about which class at the time of insurance and the presence of insured events for the entire period. When the driver has a break in driving, then when issuing the next policy, he will again be assigned the original class.
During the initial application, the calculation of OSAGO will occur from the maximum values of the indicators. That is, using a calculator, the amount will be impressive. So, the motorist is assigned the third class, while the KBM will be equal to 1. When the first year of using insurance did not show a single insured event, then the assignment of the fourth class will follow. And the coefficient indicator will drop to 0.95. If the accident took place, then the first class will be assigned, and the indicator will increase to 1.55.
This means that for one year of accident-free driving, as well as for each subsequent year, the motorist will have a 5% discount. But in the presence of accidents, the price of the policy will increase by 55%.
As a result of calculating the KBM, you need to know your class. To do this, you can contact the agency with which the insurance contract has been concluded, and there the employee will already provide the required information. And you can use other methods. After receiving all the information, you can use the calculator for the subsequent calculation.
What discounts can I get depending on the class?
So, as it has already become clear, each class has its own discount - this is clearly seen in the table.
The values will be as follows:
- Class M — discount + 145%;
- Class 0 - discount + 130%;
- Class 1 — discount + 55%;
- Class 2 — +40 discount;
- Class 3 - no discount;
- Class 4 - 5% discount
- Class 5 — 10% discount;
- Class 6 — 15% discount;
- Class 7 — 20% discount;
- Class 8 — 25% discount;
- Class 9 — 30% discount;
- Class 10 — 35% discount;
- Class 11 — 40% discount;
- Class 12 — 45% discount;
- Class 13 — 50% discount.
Summing up

In addition to one coefficient, to calculate the cost of the policy, you will need the values \u200b\u200bof other mandatory indicators, which will add up to the total amount of insurance.
One of these values is FAC. And if what KBM is is clear, then questions may arise with this value. This indicator of age and experience (FAC) will depend directly on the driver himself, and has nothing to do with a particular car. For beginners, the FAC will be maximum, as well as for young motorists who have not reached the age of 22 years.
In other cases, when the driver has a good driving experience, the FAC can also bring him a good discount. Using online calculator, for calculation on special resources, you can find out and , which will turn out next year with an increase in driving experience and the absence of accidents for the period due to the fault of the motorist.
Video instruction
Attention!
Due to frequent changes in the administrative laws of the Russian Federation and traffic rules, we do not always have time to update the information on the site, in this regard free legal experts are working for you around the clock!
CBM or bonus-malus ratio is an indicator that determines the discount on the cost of an OSAGO policy. In the people it is called a discount for accident-free driving. The indicator can increase or decrease the cost of OSAGO insurance, depending on how accident-free the car was driven in the previous year of insurance.
How to use the table to calculate the CBM?
The table for KBM calculations includes information on the OSAGO class, the value of the coefficient that corresponds to a certain class, as well as information on how the number of accidents for the annual insurance period affects the OSAGO class.
| Class | KBM | Rise in price | The number of insured events (payments) that occurred during the period of validity of previous OSAGO contracts | ||||
| – | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| A discount | The class to be assigned | ||||||
| M | 2,45 | 145% | 0 | M | M | M | M |
| 0 | 2,3 | 130% | 1 | M | M | M | M |
| 1 | 1,55 | 55% | 2 | M | M | M | M |
| 2 | 1,4 | 40% | 3 | 1 | M | M | M |
| 3 | 1 | No | 4 | 1 | M | M | M |
| 4 | 0,95 | 5% | 5 | 2 | 1 | M | M |
| 5 | 0,9 | 10% | 6 | 3 | 1 | M | M |
| 6 | 0,85 | 15% | 7 | 4 | 2 | M | M |
| 7 | 0,8 | 20% | 8 | 4 | 2 | M | M |
| 8 | 0,75 | 25% | 9 | 5 | 2 | M | M |
| 9 | 0,7 | 30% | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | M |
| 10 | 0,65 | 35% | 11 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 11 | 0,6 | 40% | 12 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 12 | 0,55 | 45% | 13 | 6 | 3 | 1 | M |
| 13 | 0,5 | 50% | 13 | 7 | 3 | 1 | M |
Using the KBM table is very simple. First you need to know the KBM. This information is available on the website of the Russian Union of Auto Insurers (RSA), you can contact the insurance company or look at the KBM in the current policy (some companies indicate the class directly in the insurance). All other sources are considered unreliable.
If a citizen enters into an OSAGO agreement for the first time, he is assigned class 3, the KBM for which is 1.00. Therefore, no discounts or surcharges apply.
Driver classes in the KBM table
The class of the driver depends on the number of insurance payments made for the previous year of insurance due to his fault. If the accident was not registered by the traffic police, this will not affect the driver's class in the KBM table, since the insurance company is interested in liability, not property.
Each insured event, which entailed the implementation of insurance payments, lowers the driver's class by 2-6 positions. For example, the driver's initial MSC corresponds to a value of 8. One accident that resulted in an insurance payment will drop the class to 5, two accidents will lower the class to 2, and three or more will drop it to the lowest level. Class M means that the client is especially dangerous for the insurance company. In this case, the cost of the policy increases by 2.45 times.
How does the OSAGO class affect the discount?
The value of the discount on the cost of the policy depends on the OSAGO class. Each year of accident-free driving entitles you to a 5% discount.
To determine what discount the driver receives, you need to do some simple calculations. It is necessary to subtract one from the value of the coefficient and multiply the resulting number by 100%.
For example, the driver class at the beginning annual term insurance - 11. It corresponds to a coefficient - 0.6. In this way,
(0,6-1)*100% = - 40%
Renewal of insurance will cost 40% cheaper.
An example of calculating the KBM according to the table
We propose to consider an example of calculating the KBM according to the table. Initial data: the driver enters into an OSAGO contract for the first time and made 2 accidents in a year that resulted in insurance payments.
Since the driver has no history, he is assigned class 3, which corresponds to the value 1. Having made 2 accidents, the class is reduced to M. When the contract is extended, the cost of insurance will be increased by 2.45 times.
The desire to reduce the cost of insurance pushes some drivers to distort information. However, this is not recommended. In the event of an insured event, the fact of participation in an accident will necessarily be revealed, and the insurance company will refuse to pay. Eliminate the consequences of the accident will have at their own expense.
Due to the fact that recently there have been big problems with the purchase of compulsory insurance policies, you can buy OSAGO online.
Before buying, we recommend that you calculate the cost of the OSAGO policy on the 2020 calculator, our calculator will not only calculate the price of the policy for you, but also show you the most profitable offer in various insurance companies.
An example of calculating the KBM for accident-free driving
At accident-free driving and the absence of insurance payments, the driver class increases by one point each year. In this case, the CBM decreases according to the table.
For example, a Class 6 policyholder has a coefficient of 0.85. After a year of accident-free driving (only accidents that occurred through his fault are taken into account), he will receive a category “7” with a multiplier of 0.80.
An example of calculating the KBM in case of accidents
The calculation of KBM in the presence of accidents is just as easy. If a motorist has four or more traffic accidents in a year, then the class drops to the lowest point "M". If from one to three accidents are initiated, then the MSC table is used to calculate the category.

For example, a class 10 insured with a multiplier of 0.65 initiated two accidents in one year. As a result, his category dropped by 7 points to "3" with a coefficient of 1.
The class is reduced only in cases where the driver is guilty of an accident.
How MSC affects the amount of contributions
The "Bonus-Malus" coefficient can both reduce and increase the cost of OSAGO.
It happens in the following way. The base value of the contribution is multiplied by the value of the MSC. When the coefficient is greater than zero (categories "M" and 0-2), the price increases. When it is less than zero (categories 4-13), the driver is given a discount. In the third class, the base fare does not change.
How to calculate KBM with unlimited insurance
"Bonus-Malus" with open insurance, that is, without restrictions on the number of drivers, is equal to the value of the KBM of the car owner. It changes according to the same rules as for a regular policy, but the discount applies only to a specific car.
Let's say you are the owner of a Nissan car and have issued an open OSAGO for it. After a few years, you received a category 10 and a 35% discount. Even though people with other classes - lower or higher - may also drive the transport, your indicator is used to calculate the cost of contributions. But when buying a second car, for example, Renault will have to earn a discount “from scratch”, from the third class, regardless of what category the Nissan had.
At the same time, another special multiplier is also used for open OSAGO. In 2019, it is equal to 1.87. This means that unlimited insurance will be 80% more expensive than regular insurance (excluding other coefficients).
Now in the market of compulsory automobile insurance among the people of OSAGO, it’s just “what the hell”. If in 2007-2009, as I remember, it was easy and simple to get insured, now IT IS SIMPLY REALLY DIFFICULT! Of course, the government is trying to put things in order by buying an electronic policy, but it works, as it turns out, not in all companies, although it seems like from 2017 they will oblige everyone. But in order to insure an ordinary ordinary driver, it is necessary to know your driver class or, as insurers call it, their bonus-malus coefficient (abbreviated as KBM). But with this, 90% of drivers have a big problem! Although everything seems to be elementary! BUT I decided to tell you how to actually calculate it yourself. The information is very useful, so read, add to bookmarks ...
Exactly what pisses me off the most. I had OSAGO insurance in the ZHASO company, I was insured in this organization for a very long time - I have an accident-free experience, about 9 years! The renewal of the policy in this company, for drivers like me, took place in a maximum of half an hour. That is, I drove up and took shape for another year, quickly and conveniently. But the whole problem is that since 2016 the company has ceased to engage in insurance specifically for OSAGO, and has transferred all cases to SOGAZ. I decided to call there, to which I was told - today you won’t have time (I called at 13.00), come in the morning before opening an hour, then maybe you can insure this day! FUCK! Like the queues are just huge - PEOPLE STAND FOR TWO DAYS! And what is most offensive is in almost any organization, no matter where to call. I have been monitoring the market all day
Electronic OSAGO
“Okay,” I thought, they immediately began to apply the electronic OSAGO policy. I am a progressive person with the Internet on "YOU", I think it's easy and simple to insure. But it wasn’t there, almost all companies only prolong OSAGO through official websites, but we are talking about ordering a new one, for a newly applied one - THERE IS NO SUCH! Just some tin. It's embarrassing to the core.

Therefore, I had such a question - the government has more than doubled prices for OSAGO, but in reality it has become even worse. Previously, in 2008-2009, there were no problems getting insured! Came and in half an hour you have a policy on hand! What has changed now? Please answer me, and why there is no article in the law that outlines the terms for issuing a policy, for example, no more than 30 minutes or without fail via the Internet. It turns out this is another traffic police, where you can wait for inspectors to the scene of the accident for hours !!! It seems that - an elementary procedure is specially complicated, WHERE IS THE CONTROL OF AUTHORITY ???
Okay, I think from January 1, 2017, SALES VIA THE INTERNET WILL REALLY COME! That is, as I see it, I went to the site, filled out the form on the site, paid from the card or electronic money and printed the policy at home! If the traffic police inspector stops, and if there is no fake, you will go further. I THINK PEOPLE WILL JUST SAY THANK YOU AND LEAVE THESE UNREASONABLE HUGE LINES!
In the meantime, there are no NORMAL calculators on the websites of companies, let's use the calculator on the PCA website, after all, this is a controlling organization.
How to calculate OSAGO?
Actually, everything is simple, we go to the PCA website and see the inscription "OSAGO Calculator". We pass and we see many not difficult fields. Such as:
- Vehicle owner
- Vehicle type
- Engine power
- Contract term
- Period of use
- Driver class
- A few points about the region and the city
- Further information about the drivers, if two or three then we drive in all

Actually below is the amount that you need to pay. BUT REMEMBER THIS IS THE RECOMMENDED BASIC AMOUNT, THAT IS THE INSURANCE COMPANY CAN BOOST YOUR INTEREST FROM THE TOP!
You can even print out the calculation and contact the insurance company with it, but there is an incomprehensible item - namely, "DRIVER CLASS". What is it and where to get it from? Let's figure it out
OSAGO driver class on the RSA or KBM website
Actually it is not difficult to calculate this driver class! And if you speak correctly, then this is - Bonus-Malus coefficient . Why it is called that way, everything is simple - if you ride for a year without accidents, then they give you a “Bonus” - a 5% discount for the next year, and if you have an accident (or two or three), then you are punished by increasing the insurance coefficient (this is understandable "Malus").
Now it's gone useful information for those who do not understand how to calculate it, look at this KBM plate.

There are only 15 levels in it, starting with "M", further from "0" to "13" inclusive.
Actually, if you are a novice driver - you have just passed on the rights, then the maximum KBM will apply to you, this zero level , the coefficient for you will be 2.3! Just think about it, that is, if the rate on your car, for example, is 4,000 rubles, then you will need to pay 4,000 X 2.3 = 9,200 rubles.

We have been driving for a year, without accidents, you are assigned a “1” driver class. And if you look at the table, then the KBM will be equal to - 1.55

The third year of accident-free experience - "3" driver class, KBM - 1

If you follow the rules and ride for 15 years without accidents, then the maximum driver class is “13”, a possible 50% discount! That is, you KBM - 0.5. So if the base rate for your car, for example, is 4,000 rubles, you will pay only 2,000 rubles, not bad, right?

This is how the driver class is calculated, which is characterized by KBM. But what if you had an accident, and it was your fault?
Boosting calculation
Everything is also simple here, again we look at the table, there are both increasing and decreasing coefficients.
Suppose that you are a disciplined driver with an experience of 8 years, your driver class is "7" (after all, there is also a zero level), which means that your KBM is - 0.8

Well, this happens, you got into one accident, and it’s your fault, that is, the insurance company paid money for a damaged car, it doesn’t matter if it’s badly damaged or just a “struck bumper”, then next year you will have an increasing KBM from the table, this is the fourth column (one payment) - you are awarded the "4" driver class. If you have made two accidents in a year, then the fifth column is “2” class, but if there are three or more accidents, a penalty KBM is awarded, class “M”.

What is class "M" - this is a penalty indicator, usually this is how insurers designate problem drivers, those who constantly hit their cars. As you can see, he has the largest coefficient - 2.45

From myself, I’ll tell novice drivers (zero class) it’s very difficult to get out of this level, that is, until you know how to drive, there is a high probability that you will strike any car and end up in the “M” class penalty area. So be careful and be careful again.
Transfer to another company and KMB
Many people worry when moving from one company to another for their discount, or rather, for their class or KMB indicator. However, there is nothing to worry about here. When you pass your former company must provide you with your KMB score. If they rested and say that this is supposedly secret information, then you can get it from the representatives of the RSA (Russian Union of Motor Insurers), because your entire insurance history should now be stored there.
Therefore, insurance upon transfer to another company should start exactly from the indicator at the end of the previous year. Let's say you left with a "5" class, so you should start with it.
By the way, now many insurance policies indicate your CBM at the end of the period, this is also information for a new insurer.

So for reference, the OSAGO law began to work on July 1, 2003, so those who have been insured since this year and are accident-free drivers have easily already accumulated a 50% discount.