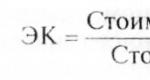UTII coefficients: k1, k2. Features of determining the k2 coefficient for UTII Calculation of UTII coefficient k2
One of the main advantages of the UTII regime, which is available for selection and, is the simplicity and accessibility of determining tax payments. The main indicators of the tax formula are fixed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and adjustment factors for calculation must be approved before the start of the calendar year.
What is the K2 coefficient for UTII
The K2 coefficient is one of the most complex parameters included in the formula for calculating the UTII tax. It should reflect numerous features of entrepreneurial activity, based on the specific operating conditions of the enterprise or individual entrepreneur.
Municipal authorities are authorized to determine the correction coefficient K2. Its effect extends only to the territory of a specific municipal entity and can vary significantly even for neighboring districts of the same subject of the Russian Federation.
The approval of the numerical value of K2 occurs for a period of at least one calendar year, ranging from 0.005 to 1. The determination of a specific numerical indicator depends on the conditions of business.
Concept and essence
 In accordance with Art. 346.27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following conditions and are used as part of the indicators for establishing the K2 parameter:
In accordance with Art. 346.27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following conditions and are used as part of the indicators for establishing the K2 parameter:
- range of goods and services offered;
- time of activity (seasonal nature of work);
- working hours;
- features of the place of work, as well as a lot of other indicators.
The main purpose of introducing the adjustment parameter K2 is the ability of local authorities to provide support measures to certain categories of entrepreneurs or organizations depending on their operating conditions. The value of the coefficient K2 cannot exceed 1, therefore, it is a reducing indicator to the fixed one.
The ability to reduce the tax burden for business entities by reducing the K2 indicator is due to different operating conditions in different regions. Taking into account the specifics of doing business is carried out at the stage of preparing and justifying the decision to approve the K2 coefficient for the coming calendar year
Regulatory regulation
- The basic rules for approving the K2 indicator are regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- In addition, the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2015 No. 03-11-11/8130 directly indicates that the approval of the K2 coefficient for the coming calendar year is within the competence of the representative authorities of municipalities.
How to recognize him
Since the K2 indicator is approved at the local level, finding out its value is not as easy as other components of the calculation formula. The decision of the local representative body on the issue of approval of the K2 coefficient is a normative legal act and is subject to mandatory publication in the manner determined by the Charter of the municipality.
As a rule, publication is carried out on the official website of the municipality or in the official printed publication of local authorities. In addition, information about the value of K2 is necessarily sent to the territorial body of the Federal Tax Service, where the taxpayer can find out the necessary information at any time.
On the official website of the Federal Tax Service, such information is available in the form of texts of regulatory acts of municipalities. To do this, you need to select the subject of the Russian Federation in which the activity is carried out.
Calculation and application algorithm
 The decision to approve K2 can only come into force from the beginning of the year for which it is established; such a tax regulation does not have retroactive effect. An exception is made for decisions in which the K2 indicator changes downward within a calendar year. This requires that such a decision expressly indicate the date of entry into force of the decision of the local representative body.
The decision to approve K2 can only come into force from the beginning of the year for which it is established; such a tax regulation does not have retroactive effect. An exception is made for decisions in which the K2 indicator changes downward within a calendar year. This requires that such a decision expressly indicate the date of entry into force of the decision of the local representative body.
As an example, we can calculate the amount of UTII for an entrepreneur providing household laundry services in the Volokolamsk district of the Moscow region. For this municipal formation, the K2 coefficients were approved by the decision of the Council of Deputies of the Volokolamsk Municipal District dated September 29, 2011 No. 43-282 and for the specified category IP are 0.5 for rural settlements.
Thus, for such an entrepreneur, the amount of the monthly payment will be: 7500 (basic profitability for household services) x 1 (number of employees) x 1.798 (for 2017) x 0.5 (K2 for the place of business) = 6742.5 rubles per month.
If the K2 indicator changes up or down, the amount of the monthly payment will change accordingly.
How to determine the size of the K2 coefficient for UTII for retail trade and other types of activities is described in this video:
The article will discuss the K2 coefficient for UTII. What kind of indicator is this, where is it used, and how to calculate it - further.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
If an individual entrepreneur uses UTII in his activities, he will need the K2 coefficient. Each municipal district has its own and differs from others. How to find out the indicator and how to calculate it correctly?
Basics
This indicator is used if an individual entrepreneur or organization has applied for the use of a single imputed tax and received a notification that it has been approved.
You cannot ignore the coefficient when filling it out, since the tax amount will be incorrect, and this will be a reason for imposing a fine.
Reporting under this regime is submitted once a quarter to the tax office. That is, when carrying out business activities, the K2 coefficient is used at least 4 times a year.
The value of the coefficient can change up or down. If the K2 value decreases and becomes less than 1, then there are several reasons:
An increase in K2 occurs in the following cases:
If there is no coefficient at all, then the tax is calculated without it. That is, UTII is calculated based on basic profitability.
At the end of each quarter, either the organization files a tax return. This is a document consisting of 3 pages. It states:
- details of the taxpayer and the tax service;
- basic profitability;
- indicators K1 and K2;
- number of days in a quarter – broken down by month;
- deduction (if any).
The final page indicates the total payment amount. The document indicates a code that allows you to control received payments.
If it is indicated incorrectly, the payment will not reach its destination. The difficulty in determining K2 arises from the complexity of individual decisions when legislators use several parts to calculate the coefficient.
To avoid confusion, for correct calculation you need to know:
If the taxpayer believes that the amount of imputed income is high, he has the right to contact local government officials with a request to lower the figure.
The basic UTII tariff for each type of activity is contained in Article 346.29 (clause 3).
What is it
These are:
- work, and goods that are offered;
- season and mode of activity;
- size received;
- features depending on the place of work;
- usable area of the electronic information board;
- number of vehicles;
- trailers and river boats, other features.
The value of the coefficient is approved by each municipality independently of each other - district, district, city. Moscow is an exception; this indicator has not been used here since 2014.
The duration of the indicator is not established, but sometimes municipal authorities set it for a specific year.
It happens that K2 for UTII is not approved. In such cases, the basic profit ratio is taken into account. It was approved in the Tax Code () for each type of activity.
If the coefficient has been approved, but the normative act has not yet entered into force, the indicator from last year is used.
Local authorities can divide the K2 coefficient into sub-coefficients. In this case, to determine the K2 indicator, they are multiplied among themselves, and the resulting value is rounded to 3 digits after the decimal point.
The value of the coefficient can be found in the tax service at the place of business activity or on its official website.
Where is it used?
Imputed income is calculated taking into account the deflator coefficient. This is an integral part of the formula when calculating. The UTII tax is not tied to the actual income of taxpayers.
The calculation is based on the basic yield. The coefficient has no effect on taxation with a size equal to 1.
If the indicator is lower, it significantly affects UTII. Functions of the K2 indicator:
That is, K2 is an effective tool for regulating the economic situation in regions and cities.
The value of the K2 coefficient for UTII
The legislation does not limit local authorities in establishing the K2 indicator. The government has the right to set both the specific value of the coefficient and its individual components.
As practice shows, the K2 value is set based on the level of employees.
If the authorities have established a separate K2 value, tax payers must calculate the final K2 amount independently.
According to general rules, the value of the coefficient should remain unchanged throughout the year. The value can be from 0.005 to 1.
To find out your indicator, you need to go to the website of the Federal Tax Inspectorate and select the section “for certain types of activities.”
Next, select the subject in which business activities are conducted and select the subsection “Features of regional legislation.” A list of legislative acts will be issued for each municipality in the selected region.
Has it changed in 2019 (table)
In the table below you can see how the federal deflator coefficient changed.
Tax legislation stipulates that the indicator is approved by the federal government taking into account the growth of inflation. The Tax Code establishes that the K2 value cannot be higher than 1 and less than 0.005.
That is, the maximum tax amount for a business can be reduced or maintained at the maximum level. In rural areas the coefficient is lower than in the city:
Compared to previous years, this year K2 increased from 1.798 to 1.868. The K2 coefficient for UTII for 2019 in St. Petersburg has the following values:
This list is not exhaustive. UTII in St. Petersburg depends on the type of activity and the area where it is conducted.
Self-calculation is not allowed this year.
Video: changes to UTII
If entrepreneurs decide to do this, an overpayment is possible. It will be difficult to return the excess amount.
How to calculate correctly
When calculating UTII, several nuances are taken into account:
- if there is more than one type of business, the maximum K2 is taken;
- if the coefficient has not been established for the current year, K2 for the previous year is taken;
- You will need not only K2, but also K1.
K1 is an increasing coefficient, and K2 is a corrective one, towards a decrease.
How to calculate K2 for retail? You will need a formula:
For individual entrepreneurs, the calculation is easier. For example, if he is engaged in the transportation of passengers, the number of boarding seats is multiplied by 1,500 rubles. To calculate, you can use an online calculator.
Calculation examples
Situation No. 1. The company carries out retail sales of goods (household appliances and office supplies). The area of the outlet is 150 sq.m. in the region of operation, a transition to a single imputed income is possible.
The sub-ratio in this district is:
Since the summer, the retail facility has been converted into a warehouse. The organization was deregistered on February 16. In January, the company worked seven days a week.
The K2 indicator for the first quarter is calculated as follows:
The indicators are summed up - (0.8+0.414)/2=0.607. Situation No. 2. The organization conducts business activities for the transportation of goods. K2 is equal to one.
The number of vehicles used is 6. The size of the database is 6 thousand rubles per unit of transport, K1 is 1,798. The work took 3 months.
The tax amount is calculated as follows: BD - 6 thousand, FP - 6, number of months - 3, coefficient K2 on UTII for the 1st quarter of 2019 - 1.
The single tax on imputed income is a special type of tax that is paid only when carrying out types of business activities approved by law. It is calculated taking into account at least seven indicators. Among them are coefficients K1 and K2 (UTII). In 2019, these indicators changed in some regions. Let us dwell in more detail on the grounds and reasons for changing the adjustment values, and also see how the K2 coefficient for UTII for 2019 affects the amount of tax payable.
Sizes K1 and K2 according to UTII for 2019
The table below will help you understand how K1 - the federal deflator coefficient - has changed over the past few years. Tax legislation stipulates that this indicator is approved by the federal government, taking into account the growth of inflation. Although some time ago officials made concessions and did not increase the calculated data, for 2019 they will not make any concessions to business.
As for the K2 coefficient, it is approved by regional authorities. The legislative and executive authorities of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation must take into account as much as possible all the conditions in which entrepreneurs operate, for example, the “profitability” of the location of the facility, transportation routes, the number of potential buyers, their solvency, seasonality and work schedule.
IN clause 7 art. 346.29 Tax Code of the Russian Federation it has been established that the size of K2 cannot exceed 1 and cannot be less than 0.005. That is, in fact, regional authorities are allowed to either lower the maximum tax amount for businesses or maintain it at the maximum level. The constituent entities of the Russian Federation themselves use the regional deflator in order to influence the decisions of entrepreneurs on where it is more profitable to open a business and in what specific area. Based on the established indicators, it is easy to notice that for rural areas the basic profitability coefficient K2 is lower than for cities, and the provision of household services, for example, is much more profitable than passenger transportation. As you can see, officials offer lower taxes to those individual entrepreneurs and companies that agree to work in small localities.
Let's look at specific examples of how K2 UTII differs in 2019 in St. Petersburg, depending on the type of activity and place of provision of services. We emphasize that the list presented is incomplete. The given values of K2 for UTII for 2019 (table below) are excerpts from the current version of the Law of St. Petersburg dated June 17, 2003 No. 299-35.
|
Type of business activity |
K2 coefficient values for municipal districts |
K2 coefficient values for cities and towns |
|
Sewing and shoe repair |
0,4 |
0,2 |
|
Manufacturing of jewelry, costume jewelry, their repair |
0,8 |
0,6 |
|
Any photo services |
0,6 |
0,4 |
|
Washing and dry cleaning |
0,4 |
0,2 |
|
Repair, maintenance and washing of vehicles |
1,0 |
1,0 |
|
Cargo transportation |
1,0 |
1,0 |
|
Transportation of passengers |
0,25 |
0,25 |
It is important to understand that you do not need to independently calculate K2 UTII in 2019 - this is not provided for by law. Entrepreneurs, of course, can “not bother” and pay taking into account K2, which will be equal to 1. But this can lead to overpayment, and it is quite difficult to return the excess amount.
Therefore, it is better to find out this indicator in advance. There are two ways to do this. The first is to contact the INFS at the place of registration and consult on this issue. The second is to use the Federal Tax Service website. Select your subject in the upper left corner and select the information you are interested in: all regional features of UTII, indicating the details of specific documents, are given taking into account the latest changes in legislation.
Practical application of K2, or how the coefficient affects the amount of UTII
Why is it so important to know the regional coefficient? Because it directly affects the amount payable. Here is the formula for calculating tax for the quarter:
Σ = (DB × K1 × K2 × (FP1 + FP2 + FP3)) × 3 × UTII rate,
- BD - monthly basic profitability (set for each type of activity in clause 3 art. 346.29 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- K1 and K2 - coefficients changing by decision of federal and regional authorities;
- FP1, FP2 and FP3 - physical indicators in each of the three months of the quarter (area, number of employees, number of machines);
- 3 — number of months in a quarter.
For example, let’s take two individual entrepreneurs, individual entrepreneur A.S. Ivanov. and individual entrepreneur V.K. Petrova, who work for UTII in the city of Zelenogorsk (the city belongs to St. Petersburg). Petrov repairs shoes, and Ivanov provides photographic services. For both, the basic income per month is 7,500 rubles, since both types of activities relate to household services. Both have no employees. In 2019, they have a common K1 on UTII of 1.915, and the tax rate is also the same - 15%. Let's calculate who will pay how much to the budget, taking into account that K2 for shoe repair is 0.2, and for the provision of any photographic services - 0.4.
Calculation for individual entrepreneur A.S. Ivanov per quarter:
(RUB 7,500 × 1,915 × 0.4 × (1+1+1 (employees))) × 3 × 15% = RUB 7,755.75
Calculation for individual entrepreneur V.K. Petrov per quarter:
(RUB 7,500 × 1,915 × 0.2 × (1+1+1 (employees))) × 3 × 15% = RUB 3,877.9
The obtained figures show that in Zelenogorsk it is more profitable to provide photographic services than to repair shoes. At least from a tax perspective.
What are the coefficients K1 and K2 in imputation? Where should I look for the K2 coefficient for UTII for 2016?
Deflator coefficient K1 and K2 for UTII
By studying the features of taxation of small businesses in Russia in general and individual special regimes, we must figure out what taxes or what form of taxes we should choose when running our business.
Today we will continue the conversation on the topic of what UTII is and we will analyze the UTII correction coefficients, the so-called K1 and K2 for different regions and cities.
Correction coefficient K1 for UTII
The base rates on the basis of which imputed income is calculated are strictly fixed in the tax code of the Russian Federation and can be changed only through amendments to it. But the economy is a living organism in which constant processes occur, including such as rising industrial prices, inflation, and so on. Ultimately, such processes lead to the depreciation of any fixed rate expressed in natural units, in the single tax these are rubles. It is precisely in order to ensure the relevance of the rate and maintain it at an economically justified level that the adjustment coefficient K1 is changed in UTII.
Based on the economic essence of UTII K1, it should increase imputed income by the amount of the increase in industrial prices last year. In order to explain this in human language (let’s forgive economists), everyone knows what inflation is (increasing prices for retail goods), but industrial prices are also rising, and it is on the basis of rising industrial prices that the K1 coefficient is adjusted.
The adjustment of the deflator coefficient for UTII is carried out by the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia, or rather, it would be more accurate to say that by its order it establishes these indicators for all taxation systems in the country.
For 2014, the adjustment coefficient K1 for imputation was established by ORDER No. 652 of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated November 7, 2013 and is equal to 1.672.
For comparison:
- UTII deflator coefficient in 2013 was 1.569
- UTII deflator coefficient in 2014 is 1.672
- UTII deflator coefficient in 2015 is - 1.798
- The UTII coefficient for 2016 is 1.798 (initially it should have been 2.083) about the vicissitudes of the adoption of the order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated October 20, 2015 No. 772
For reference, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, coefficients are set until November 20 for the next budget year; if such an order has not been adopted, the validity of last year’s order is automatically extended.
Conclusion: the K1 coefficient is set once a year, until November 20, and is increasing.
Correction coefficient K2 for UTII
More details about the indicators themselves are a little lower, and now for those who are looking for a specific indicator in their region. The total number of K2 indicators for all regions and municipalities is enough for a thick book, perhaps even more than one. As a result, it is not physically possible to post them.
The conditions for patents and the simplified tax system have changed significantly, plus tax incentives for small businesses have actually appeared in Russia.
Unlike K1, the adjustment coefficient K2 is reducing and is designed to equalize the business of those working in different regions of the country. Of course, it is impossible to compare the working conditions and gross revenue of a store in a metropolis and a small retail outlet in a small town. It is with the aim of equalizing rights that K2 was introduced, which is essentially a lowering one and can be set at level 1 or lower. The decision on what the size of this indicator should be for imputation is made by local authorities depending on the economic situation in the region.
Practice shows that once it has been approved at a certain level, local authorities do not make changes for certain types of activities; this is where there is room for initiatives on the part of small businesses. Who is stopping you and your friends from contacting regional authorities with a request to reduce it for next year?
If today the K2 adjustment factor for UTII (2015 and 2016) in your region is 0.8, by reducing it, for example, to 0.7, how much can you save on taxes.
There is a civil society, and there is no politics here, because local authorities, when approving them, took “average ceiling” figures and no one can explain why exactly this.
Conclusion: the K2 coefficient is reducing and is designed to equalize the work of businesses in different regions of the country; if you think that you have a large single tax, go to the local authorities and demand a reduction in this indicator. It is worth noting that local authorities approve the K2 coefficient once a year until November 20 for the next financial year, and if you want to revise it, this can be done already for 2017.
One more thing, if you need to find out K2 for 2016 in your region, then you should contact the local tax service and take the appropriate decision, in which the deflator will be prescribed for your region and by type of activity. Unlike K1, the deflator for the single tax K2 is adopted by type of business activity.
Additionally, I can say that decisions of municipal councils can be found by logging into your personal electronic account on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
The main difficulty in determining K2 in 2016 may lie in the “intricacy” of individual decisions, where legislators use several components when calculating the reduction factor. To begin with, you should clearly understand what you need to know:
- type of activity. In some cases, including the product range.
- address of the activity. Not just an address, but also a district in accordance with the decision of municipal councils; in most cases, they independently divided them into districts depending on the “profitability” of the place.
- number of employees.
It is interesting that the maximum size of the decreasing deflator K2 is 1, but the minimum can be 0.05, so this is a huge reserve for reducing the taxation of small businesses in a particular region, especially considering that part of the single tax can be covered by the payment of a pension payment.
Based on materials from: http://pilotbiz.ru
To calculate UTII obligations, in addition to basic profitability and physical indicators, it is necessary to take into account adjustment factors:
- K1 – its size is established annually by order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation (1.868 – for 2018);
- K2 (UTII) - the value of the coefficient is regulated by regional authorities, broken down by type of activity and other indicators. Its basic size is fixed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the maximum value of the K2 coefficient for UTII can be in the range of 0.005-1 (Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The minimum period for which the coefficient is set is 1 year.
The reduction coefficient K2 for 2018 (UTII) in some constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities has been changed; let’s look at its current values for a number of regions.
How to find out K2 for UTII 2018
In order for the calculation of the tax payment amount to be correct, it is necessary to substitute the current parameters of the coefficient values into the calculation formula. According to UTII K2 (2018), valid in the region, you can find out on the website of the tax service. To do this you need:
- go to the website ]]> tax.ru ]]> – K2 for UTII can be found if you select the tab with the list of taxes in force in Russia, go to “Special modes” and select the “UTII” item;
- at the bottom of the page there will be a block of information about regional peculiarities of legislation. It provides links to regional regulations establishing an “imputed” regime in the relevant territory, as well as the K2 coefficient for UTII for 2018 for a specific municipality.
If no “fresh” decisions or resolutions on the coefficient were made for 2018, then the K2 values of the previous year remain in force. If in the section with regional features there is no mention of new regional legal acts on UTII, K2 for individual entrepreneurs in 2018, as well as for legal entities, is applied in the value that was in force in 2017. If the size of K2 in the region is not established, its value is accepted equal to 1.
K2 according to UTII for 2018: table
All subjects of the Russian Federation can set their own values for coefficient indicators, with the exception of Moscow - UTII is not valid in the capital. For one type of activity, several coefficients can be applied, which in general should not exceed the maximum value of 1.
It is quite difficult to present here in the form of a single table all the K2 operating in the Russian Federation - taking into account the total number of municipalities and types of “imputed” activities, such a table will contain a huge number of indicators. We will provide current K2 coefficients for some regions.
For example, K2 for 2018 (UTII) of St. Petersburg is fixed by the Law of St. Petersburg dated June 17, 2003 No. 299-35 (updated by the provisions of the law dated February 22, 2017 No. 103-15). This is what the table of basic coefficient values for St. Petersburg looks like:
|
Area of activity |
Range of values of UTII K2 St. Petersburg (depending on the address) |
|
Household services |
From 0.4 to 0.6 |
|
except: |
|
|
From 0.2 to 0.4 |
|
|
|
From 0.6 to 0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Veterinary services on the territory of the veterinary hospital |
|
|
Veterinary services at the client's premises |
|
|
Repair, maintenance, car wash, parking services, cargo transportation |
|
|
Transportation of passengers |
|
|
Retail trade on trading floors with an area of up to 5 sq.m.: |
|
|
From 0.2 to 0.4 |
|
|
|
From 0.2 to 0.4 |
|
Retail trade on trading floors with an area of more than 5 sq.m.: |
|
|
From 0.1 to 0.2 |
|
From 0.2 to 0.3 |
|
|
|
Catering industry |
|
|
From 0.2 to 0.25 |
|
|
Renting out retail outlets |
From 0.55 to 1 |
|
Retail trade in the premises of retail chains: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following table systematizes data on the coefficients of some cities:
- K2 (UTII) in 2018 in Perm is regulated by the Decision of the Perm City Duma dated November 29, 2005, No. 200 (as amended on November 19, 2013). The values for EBND K2 (2018) within this city are divided into 4 zones. The address of objects in each zone is specified in Appendix 2 of Decision No. 200.
- K2 (UTII) in 2018, the Stavropol Territory represents 35 municipalities. The table provides information on K2 UTII in 2018 Stavropol - City Duma decision dated November 11, 2005 under registration No. 148 (as amended on May 31, 2017).
- K2 for 2018 (UTII) Kursk is regulated by the Decision of the Kursk City Assembly dated November 25, 2005 No. 171-3-RS (as amended on January 24, 2017).
- For K2 (UTII) in 2018 in Voronezh, it is necessary to focus on the norms of the Decision of November 16, 2005 No. 179-II (as amended on November 1, 2017).
- K2 for 2018 (UTII) Saratov - the values of key indicators are recorded in a separate document for each municipal district. In Saratov, City Duma Decision No. 64-630 dated November 8, 2005 (as amended on November 18, 2016) is in force.
- K2 for 2018 (UTII) Murmansk - the regulatory function is performed through the Decision of the Council of Deputies dated November 7, 2005 No. 13-158 (as amended on January 26, 2017).
- K2 for UTII for 2018 Tambov - you need to rely on the indicators reflected in the City Duma Decision No. 75, dated November 9, 2005 (as amended on November 29, 2017).
- K2 for UTII for 2018 Penza - the regulatory act is City Duma Decision No. 240-16/4 with the publication date of November 25, 2005 (as amended November 30, 2017).
- K2 for 2018 (UTII) Belgorod - the values of the parameters required for calculating the tax liability were approved by the Decision of the Council of Deputies No. 658, dated October 30, 2012 (as amended on October 30, 2012).
- The values of the K2 adjustment coefficients for 2018 (UTII) of Arkhangelsk are presented in Decision No. 67 with the publication date of November 29, 2005 (as amended on November 30, 2016).
Table:
|
Types of activities |
UTII coefficient K2 (2018) depending on belonging to the territorial zone of Perm |
K2 for 2018 (UTII) Kursk region (Kursk) |
K2 for 2018 Voronezh |
K2 (UTII) by type of activity in Saratov |
K2 for 4 address zones in Murmansk |
K2 for 2018 Tambov |
K2 in 6 zones of Penza |
K2 for 2018 Belgorod |
Size K2 (UTII) for 2018 Arkhangelsk |
K2 for 2018 Stavropol |
|
Household services |
From 0.281 to 1 |
From 0.5 to 0.8 |
From 0.14 to 0.8 |
From 0.03 to 0.61 |
From 0.6 to 0.8 |
From 0.13 to 0.8 |
From 0.18 to 0.81 |
From 0.05 to 1 |
From 0.33 to 0.67 |
|
|
Veterinary services |
From 0.35 to 1 |
From 0.03 to 0.31 |
From 0.22 to 0.42 |
From 0.2 to 0.8 |
||||||
|
Repair, maintenance and car wash |
1, if the number of personnel does not exceed 5 people |
From 0.93 to 1 - repair and maintenance |
From 0.37 to 0.75, if the number of hired personnel does not exceed 20 people |
|||||||
|
0.7 with a staff of 5-10 people |
for car washes, K2 values change quarterly: |
From 0.23 to 0.57 with a staff size of 21-40 people |
||||||||
|
0.5 if the number of employees exceeds 10 people |
|
From 0.2 to 0.48 with the number of employees over 40 people |
||||||||
|
Open parking lot |
1, if the parking area is less than 600 square meters. m |
From 0.07 to 0.5 |
||||||||
|
0.7, if the area allocated for parking has an area in the range of 600-1500 square meters. m. |
||||||||||
|
0.5 for parking lots with a total area of more than 1500 sq.m. |
||||||||||
|
Closed one-story parking lot |
||||||||||
|
Multi-level closed parking lot |
||||||||||
|
Freight transportation |
From 0.65 to 1 |
From 0.27 to 0.63 |
||||||||
|
Transportation of passengers by passenger transport |
From 0.208 to 0.520 |
From 0.57 to 0.70 |
From 0.35 to 1 |
From 0.12 to 0.27 |
||||||
|
Transporting passengers on buses |
From 0.110 to 0.320 |
From 0.19 to 0.50 |
From 0.3 to 0.4 |
|||||||
|
Retail trade (depending on the type of goods and area of the retail space) |
From 0.06 to 1 |
From 0.260 to 1 |
From 0.15 to 1 |
From 0.03 to 1 |
From 0.12 to 1 |
From 0.18 to 0.9 |
From 0.55 to 1 |
|||
|
Catering services |
From 0.05 to 0.9 |
From 0.468 to 1 |
From 0.05 to 1 |
From 0.4 to 0.7 |
From 0.36 to 0.9 |
From 0.352 to 0.575 |
||||
|
From 0.250 to 0.354 |
From 0.16 to 0.6 |
From 0.005 to 0.25 |
From 0.3 to 0.4 |
From 0.1 to 0.4 |
From 0.175 to 1 |
|||||
|
Renting housing |
From 0.4 to 0.6 |
From 0.15 to 0.8 |
||||||||
|
Renting out retail properties |
From 0.250 to 1 |
From 0.5 to 0.7 |
From 0.47 to 1 |
From 0.06 to 0.48 |
From 0.6 to 0.9 |
From 0.15 to 0.5 |
Some legal acts require independent calculation of K2 (UTII) in 2018. For calculations, legislators recorded in regulatory documents the formulas and initial values of the indicators used in the calculations (several coefficients applied simultaneously). This approach is used, for example, in the following regional legal acts:
- Decision of the Tver City Duma No. 109, dated November 24, 2005 (as amended on November 23, 2016), by which it is possible to determine K2 for UTII for 2018 in Tver;
- The decision of the City Council under registration No. 502 dated September 18, 2012 reveals the algorithm of actions for introducing K2 according to UTII for 2018 in Orenburg;
- Decision No. 293 dated November 2, 2005 (as amended on November 23, 2016) adopted by the regional authorities regulates the calculation procedure for the exact value of K2 for UTII for 2018 in Omsk (the Omsk City Council put this legal act into effect by its Resolution dated November 2, 2005. No. 1182);
- K2 (UTII) in 2018 of Vologda is determined according to the rules reflected in the Decision of October 6, 2005 No. 310 as amended. dated 04/21/2016 (the authorship of the document belongs to the Vologda City Duma);
- On October 26, 2005, the Volgograd City Council of People's Deputies adopted Resolution No. 22/430 (as amended on December 24, 2014), which outlines the mechanism for calculating K2 for 2018 (UTII) of Volgograd, taking into account the basic level of profitability in various areas of business activity.
In each subject of the Russian Federation, the values of the coefficients may vary depending on the territory’s affiliation with a particular municipal entity. So, for example:
- according to K2 for 2018 (UTII), the Lipetsk region presents the differentiation of coefficient values for 20 districts;
- for K2 for 2018 (UTII), the Irkutsk region introduced 42 regulatory documents, each of which regulates the distribution of coefficients for individual municipalities;
- in relation to K2 for 2018 (UTII), the Moscow region introduced differentiation of numerical indicators for 70 districts and urban districts;
- in relation to K2 for 2018 (UTII) of the Kemerovo region, one must focus on one of 33 regulatory legal acts, each of which regulates UTII in individual localities;
- according to UTII, the coefficient K2 of Tatarstan is 45 regional decisions for municipal districts of the republic;
- to determine K2 for 2018 (UTII) of the Ivanovo region, you need to look for its value in one of the 27 legal acts issued by the authorities of municipal districts.