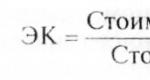How to calculate net profit for a month. How to find net profit - formula. Net profit: definition
The easiest way to determine net profit as the remainder of income from activities after paying all mandatory expenses from it. Sometimes net profit can be called “net income”, “free balance”, in the English-speaking world - “net profit”, etc.
The intrinsic meaning of net profit is that it is the ultimate goal of any entrepreneurial initiative. This is a real indicator of the commercial success of an enterprise.
Net profit can be presented in absolute terms, i.e. in monetary terms and as a percentage of other values, for example, gross income, amount of investments, etc. All options for assessing net profit may be in demand depending on the purposes of the analysis. For example, the total amount of net profit gives the entrepreneur the opportunity to decide whether the project is worth the effort; the percentage of net profit to investment determines interest in the enterprise. In the same way it is convenient to calculate internal economic processes, costs and other indicators
Net profit formula
Net profit is not an arbitrary concept. Its calculation follows clear rules. The calculation options differ only in the degree of generalization or detail of income and expense items. For example, the simplest net profit formula looks like this:
Net profit = total profit - the sum of all expenses.
The most common formula is:
Net profit = profit before tax - income tax.
Net profit = Profit before tax -/+ Income tax -/+ Change in deferred tax assets -/+ Change in deferred tax liabilities -/+ Other taxes and fees calculated from profit.
Adding a “+” sign to the “-” sign in the components of the formula is done in case the indicators of expense items have a negative value, this can happen, for example, when overpaying in past periods.
When calculating, the term “net profit” can be transformed into “loss”. In essence, this is the same concept, i.e. the result of the transaction in a positive or negative value.
Use of net profit
It may seem that net profit is the last link in the chain of calculations. This is wrong. If the net income can be claimed by more than one recipient, it becomes undistributed income. The amount of such income is subject to distribution among the owners in proportion to their shares in the total capital. This is called "earnings per share." The part of net profit not used to pay dividends is called “retained earnings”.
It is worth noting that the object of distribution can be not only net income, but also other income, including unplanned income.
In addition to dividing net profit into shares according to the number of owners, there are other options for distributing available funds. They can be spent on:
- Consumption - otherwise spending on the personal needs of the recipients. Paying dividends usually falls under this option;
- Accumulation - placing funds in bank accounts, purchasing valuables and other liquid assets;
- Investment - here we distinguish between external and internal placement of investments. In the first case, the funds are used to develop one’s own enterprise, in the second, the money is invested in third-party projects in order to receive income from such an investment.
They also sometimes talk about creating reserve funds, investing in the social sphere, etc. However, all options for using net profit can one way or another be reduced to the three categories listed above.
Net profit is a concept that applies to both small businesses and large corporations. Increasing this part of income is the main task of every businessman. To correctly calculate profit, you need to know its main indicators and be able to use a special formula.
This article will serve as a step-by-step guide to calculating your net income and analyzing the data.
Net profit: definition
Net profit is part of . This is the balance of funds after paying all mandatory taxes, fees, deductions and other payments. Due to the net share of profit, you can increase working capital, form various funds and reserves, and also make investments.
Net income is the main source of formation of the enterprise’s budget, as well as its cash savings. This indicator allows you to stimulate the team and expand production. There are many ways to use this indicator. The management’s task is to correctly distribute available finances so that they continue to bring dividends.
Net profit indicators
In order for net profit indicators to work for the benefit of the company, they must be analyzed. This will help determine the effectiveness of each of them and the business as a whole. Based on the data obtained, you will be able to determine prospects for growth, equipment modernization and product range renewal.
It will also be possible to track how production volumes affect net profit. But first things first.
Revenue for the specified period
Analysis of this indicator is called horizontal. To study, you will need the current balance sheet of the enterprise, profit statements, and the company’s financial plan. In some cases, it will be necessary to use other accounting documents.
You can analyze revenue for a month of operation, a quarter, or a year. It all depends on the scale of the business and the area in which it is represented. If these are direct sales, then every hour of work and the profit from it is important. If you are engaged in production, then it is enough to conduct such an analysis once a quarter or a year.
Thus, the revenue indicator within a certain time frame makes it possible to determine the profitability of the enterprise and develop an optimal strategy for further development.
Product cost
– an important comprehensive indicator that makes it possible to judge the effectiveness of the company’s use of its available resources and the level of organization of work at the enterprise.
The cost price is expressed in monetary format and allows you to determine the cost per unit of production. Typically, the final amount includes pre-production, manufacturing and distribution costs.
Analysis of the indicator makes it possible to determine at what stage production costs reach their maximum value and reduce them. This directly affects net profit, which can only be increased by reducing costs.
In reality, this could be the purchase of cheaper raw materials or free delivery of some components. It could also be benefits for electricity or water supply. 
Calculation of net profit. Formula
Net profit is calculated within a certain period. Just like with the total revenue indicator, this can be a quarter, a year or a month.
All data for calculating net profit is taken exclusively within the selected period of time.
The formula for calculating net profit is quite simple:
PP = AF + VP + OP – CH, Where
PE – net profit,
FP – financial profit,
VP – gross profit,
OP – operating profit,
VP = revenue – production cost;
FP = financial income – financial expenses;
OP = operating income – operating expenses.
Also, net profit can be displayed in the form of the following formulas:
PP = B (revenue) – SP (product cost) – Administrative and selling expenses – Other expenses – Taxes
PE = Profit – Taxes
The economic meaning of each of the formulas is the same, so you can use the one that seems most convenient to you. The first in this case is more detailed and will allow you to calculate all components of your income.
According to statistics, the normal net profit in business is about 14%. If this value is less, then the enterprise can be considered unprofitable. If the net profit is completely negative, then the business is definitely operating at a loss.
However, this is considered normal when a startup has just embarked on its development path and has not yet managed to return the invested funds.
Calculation example
We offer you a simple example of a business - a small publishing agency. The total profit from the books sold for the month was $20 thousand. The rights to publish some works and some custom advertising materials were also sold. This brought in another $7 thousand and $3 thousand respectively.
The company's total profit was:
$20 thousand + $7 thousand + $3 thousand = $30 thousand
The publishing house's total expenses for the current month amounted to $13 thousand.
Based on these data, you can determine net profit (NP) by simple subtraction.
$30 thousand - $13 thousand = $17 thousand.
The company received a net profit of $17 thousand.
Case Study
A company's income can be very different. This includes the sale of products and the sale of services. Also, income can be interest on deposits, etc. In our case, the publishing house receives income not only from the sale of books, but also the rights to various materials and the production of custom advertising.
It is worth considering that if any of the clients needed to pay monetary compensation, the amount would be deducted from the total profit.
Total costs also include many indicators. Include all funds spent during the reporting period. Using the example of a publishing house, this means purchasing raw materials, paying workers, electricity, renting space, etc.
As for the net profit received, in the publishing house it can be used to purchase new equipment, for example, printing presses. This will lead to an increase in the number of products produced and, in the future, to additional profits.
Thus, a one-time investment turns into a long-term investment, which in the future will help increase net profit.
Conclusion
Net profit is not just money earned, but an effective tool for developing your business. If used correctly, you will ensure rapid growth and development for the company.
Net profit can be used for the following purposes:
- replenishment of inventories;
- innovation development;
- renewal of production assets;
- creating reserves;
- investments;
- charity;
- staff development.
Return at least part of the net profit received to the business. This will lead to a stable increase in the indicator up the chart.
By tracking the dynamics, over time you will be able to enter the international arena and attract foreign investors to your project.
Business is endless statistics and graphics. Control your net profit and other indicators of your income and your business will flourish!
Net profit is the part of the enterprise's balance sheet profit that remains at its disposal after paying taxes, fees, deductions and other obligatory payments to the budget. Net profit is used to increase the company's working capital, form funds and reserves, and invest in production.
Based on the results of net profit, you can evaluate the financial condition of the enterprise; this indicator determines how much the turnover of the enterprise can be increased or decreased, as well as how much money can be invested in the development of the enterprise.
Depending on the volume of net profit, dividends are also paid to the shareholders of the enterprise.
How is net profit calculated?
Net profit is a very important indicator of the efficiency of an enterprise. Net profit is also considered to be the funds that remain at the free disposal of the enterprise after all planned expenses.
Using net profit, an enterprise can form reserve capital, purchase new equipment for the enterprise, invest in the activities of other enterprises, do charity work, and pay dividends to shareholders. Part of the available funds is also spent on rewarding employees: bonuses, vouchers, corporate events, assistance in purchasing housing, etc.
The amount of net profit depends on many factors, namely:
- The amount of total revenue at the enterprise;
- Cost;
- Amount of tax fees;
- Amount of other income and expenses.
There is also the concept of net loss, this is when an enterprise has negative profit. Many enterprises turn out to be unprofitable, despite successful activities during the year. Conversely, a small company without a huge turnover and a wide range of products can bring in colossal amounts.
How is net profit calculated?
There are many methods used to calculate net profit. Whichever way you choose to not calculate net profit, the result will be the same for all calculation methods. But in practice, a simplified formula is used, that is, the financial results statement is filled out line by line, the final line of which is considered to be net profit.
A simplified formula for calculating net profit looks like this:
PP = V – SS – UR – KR + PD – PR – NP,
B - revenue;
CC - cost of sales;
UR and KR - administrative and commercial expenses;
PD and PR - other income and expenses;
NP - income tax.
The data for calculating profit using a simplified formula can be taken from the financial performance report of the enterprise for the required period.
Let's look at how it looks in the report, and which line to fill in, using an example in the form of a table. For example, the Podsolnukh enterprise reflected the following data in its reporting:
| Indicator | Line | 2016 (thousand rubles) |
| Revenue | 2110 | 150 |
| Cost price | 2120 | 60 |
| Business expenses | 2210 | 15 |
| Administrative expenses | 2220 | 20 |
| Other income | 2340 | 2 |
| Other expenses | 2350 | 1.5 |
| Income tax | 2410 | 11.1 |
| Net profit | 2400 | 61.9 |
In this case, net profit is calculated as follows:
150 + 2 - 60 - 15 - 20 - 1.5 - 11.1 = 44.4 thousand rubles.
The formula for calculating net profit in expanded form:
PP = FP + VP + OP - N,
where PE is net profit;
FP - financial profit. It is calculated by subtracting similar expenses from income from financial activities;
VP - gross profit. Calculated as sales revenue minus production costs;
OP - operating profit. Expenses are deducted from income from other activities;
N - amount of taxes.
Formula for calculating net profit in collapsed form:
PP = P – N, where
P – profit;
N - tax amount.
Indicators that influence the formation of net profit
Net profit depends on many indicators, and judging by the calculation formula, we see that such indicators are:
- The company's revenue is the amount of money received from the buyer for the sale of products for a certain period. Revenue also includes income received from other operations that are not related to the main activity:
- interest received from the loan provided;
- income from participation in the activities of other organizations;
- income received from the sale of property and equipment;
- rent and other income.
- The costs of an enterprise that are associated with its activities. In financial accounting they are usually called:
- Costs associated with the production of products and their further sale, thereby forming the cost price;
- Costs associated with transporting goods and during the sales process, they form business expenses;
- Expenses not related to the main production are usually called other expenses.
The main costs of the enterprise include the following expenses:
- Payments to employees of the enterprise;
- Mandatory social contributions to the wage fund;
- Deductions for depreciation;
- Payment of utilities;
- Material and other costs.
Other expenses include both non-operating and operating expenses that are not related to production, but are paid at the expense of the enterprise. This expense item includes:
- Payment of interest on loans received;
- Write-off of the residual value of equipment not sold;
- Payment for training for company employees;
- Marketing expenses;
- Expenses that were associated with force majeure circumstances.
- The amount of tax deductions. Since the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for several taxation regimes, for which the types and amounts of taxes differ. An enterprise can pay taxes such as: income tax, profit tax, UTII, or even combine several budget payments depending on the type of activity.
Also, the amount of tax payments may vary depending on whether the taxpayer has tax benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question No. 1 What is net profit?
Answer: Net profit is the part of the enterprise’s balance sheet profit that remains at its disposal after paying taxes, fees, deductions and other obligatory payments to the budget.
Question No. 2: What can the resulting net profit be used for?
Answer: Using net profit, an enterprise can form reserve capital, purchase new equipment for the enterprise, invest in the activities of other enterprises, do charity work, and pay dividends to shareholders. Part of the available funds is also spent on rewarding employees: bonuses, vouchers, corporate events, assistance in purchasing housing, etc.
Question No. 3 What indicators does net profit depend on?
Answer: Net profit depends on many indicators. The main ones can be identified as follows: the amount of revenue received, cost, the amount of tax fees, other income that is not related to the main activity, as well as other expenses.
Question No. 4 What are the methods for calculating net profit?
Answer: To calculate net profit, you can use different formulas, but no matter what formula you use, you will still get the same result. Formulas come in expanded, collapsed and simplified form. But in practice, a simplified formula is used, that is, the financial results statement is filled out line by line, the final line of which is considered to be net profit.
Which entrepreneur does not know what profit is? Probably no one - this economic indicator is extremely important for the survival and development of a business.
What is operating, marginal, balance sheet or gross profit? What is the formula for calculating net profit?
Only experienced entrepreneurs and excellent students of economic education can answer these questions without any problems. And this article is intended precisely for those who want to remember half-forgotten terms or learn something new.
Determination of net profit
We should start with the basics, and one of the most important economic indicators of the success of an enterprise is net profit - the money remaining at the company's disposal after paying staff and paying all fees, taxes and bank and other deductions.
From these funds reserve funds and other savings are formed, and net profit is also used for the expansion and development of the enterprise.
Net profit and economic profit should not be confused. Their differences will be explained below.
Profit classification
The concept of profit is very diverse and it is classified according to the following criteria:
- According to the sources of formation, there is profit from the sale of its products, from the sale of means of production and other fixed assets and from other activities.
- By profit-forming elements - this sign means which items of expenses and income are taken into account in the calculation.
- Based on the nature of taxation, a distinction is made between profits on which tax is taken and those that are not taxed.
- On the basis of time, profits are distinguished for the current period, for the previous time and its planned level.
- On the basis of inflation, a distinction is made between nominal and real profits. The latter is an adjustment of the nominal value to take into account inflation for the reporting period.
Above are only the main classification criteria. If desired, this list can be significantly expanded, but as a basis it is quite sufficient.
Net profit indicators
It is not enough just to know the amount of net profit of your enterprise; you need to understand what indicators it depends on.
Being aware of this issue, you will be able to make management decisions that can significantly increase both your personal income and the amount of funds allocated for further expansion of the company, rewarding staff and saving for a rainy day.
Revenue for a certain period
The main indicator of net profit is revenue for a certain period. It consists of the money that your company receives for the sale of goods or services, investment and financial activities.
To analyze this indicator, you should choose the right period - if it comes to production, especially mass production, then it is reasonable to analyze revenue for a whole year or quarter.
 As for more “dynamic” areas of business, such as sales or the provision of services, it makes sense to pay attention to revenue for the week, month or certain seasons when a particular product or service is in high demand.
As for more “dynamic” areas of business, such as sales or the provision of services, it makes sense to pay attention to revenue for the week, month or certain seasons when a particular product or service is in high demand.
How can you influence your revenue? If demand exceeds supply, revenue increases by increasing production. In the opposite situation, you need to create advantages for your products and services over competitors.
If your company is engaged in retail trade, then in order to increase revenue it is necessary to increase the attractiveness for consumers not only of the goods themselves, but also of the store in which they are sold.
Product cost
 Cost refers to the cost of resources, human labor and equipment spent on the production of a particular product or service.
Cost refers to the cost of resources, human labor and equipment spent on the production of a particular product or service.
It also includes the costs of storing manufactured goods and transporting them.
Reducing costs is one of the main ways to increase profits.
But in the pursuit of excess profits by reducing costs, one should be careful and ensure that the quality of what is produced remains at the same level; low-quality products are less competitive.
Profit calculation formulas
 Now let's look at the types of profits that can be used in the operation of an enterprise and the formulas used to calculate them.
Now let's look at the types of profits that can be used in the operation of an enterprise and the formulas used to calculate them.
Abbreviations for economic indicators used in the formulas are given in parentheses.
Gross profit(VP) is the difference between revenue (B) and cost (C) of goods sold. It shows how much revenue from sales exceeds the costs of its creation and implementation. Calculated using the following formula:
Operating profit(OP) is the money received by deducting from the gross profit management (U), commercial (C) and other (P) expenses that are not directly directed to the manufacture of goods (collectively they are called operating expenses).
OP=VP-U-K-P
Balance sheet profit(BP) is profit, in which the calculation takes into account not only income from the main activities of the enterprise, but also income (or losses) from other activities of the company. The latter include the sale of fixed assets of the enterprise, investments and other financial transactions. Net profit has the following formula for calculating the balance sheet:
BP=PRP+PPR+PVO,
where PRP, PPR and PVO are profits from sales of products, sales of fixed assets and operations not related to sales, respectively.
Profit from sales(PoP) is the difference between gross profit and selling costs and administrative expenses (U).
Taxable income(NP) is the profit on which tax is levied. It is calculated as the difference between gross profit and income that is not taxed (NON), as well as the amounts of tax benefits (NL), if any.
NP=VP-NON-NL
Marginal profit(MP) is the difference between sales revenue and variable expenses (PR):
Variable costs are costs whose volume is related to the quantity of products produced.
retained earnings(NP) is the amount of cash that remains after taxes and is not distributed among shareholders as dividends. It is used to increase fixed assets and develop the enterprise. It is calculated as the difference between net profit (NP) and the amount of dividends paid (D):
Estimated profit- this is the amount of money included in the construction estimate and intended for the development and modernization of the construction organization’s production and additional stimulation of its workers. When calculating it, one should be guided by the guidelines for determining the amount of estimated profit in construction (MDS 81-25.2001).
Economic profit(EP) are the funds remaining with the company after deducting all costs, including opportunity costs, from total income. Total income (CI) includes revenue from sales, income from the sale of fixed assets, financial and investment transactions. As for expenses, in addition to explicit costs (EC) for wages and the purchase of materials, there are opportunity costs (or implicit costs, abbreviated NI), which express the possible lost profit from choosing one or another option for capital distribution.
EP = SD – YAI – NI.
And in this topic we will get acquainted with the concept of the current liquidity ratio and learn how to calculate it correctly.
Algorithm and formulas for calculating net profit
 First, decide for which reporting period the calculation will be made: year, quarter or month.
First, decide for which reporting period the calculation will be made: year, quarter or month.
A shorter period allows you to assess the current position of the enterprise and the results of its recent work; a longer reporting period allows you to consider the development trends of the company and provide the basis for planning its future activities.
Now we determine sales revenue, production costs, operating expenses and the amount of taxes and other fees. The formula for calculating net profit ultimately looks like this:
PE=V-S-OR-N
If your company receives income from investments, sales of assets and other non-production activities, income and expenses from these operations should be included in the calculation of net income.
The procedure for calculating the rate of return
The rate of profit (Np) is the ratio of profit (P) for a certain period to the advanced funds (AS).Advanced funds consist of the costs of production of goods and wages for the reporting period.
The result of the ratio should be multiplied by 100%:
Np=(P/AS)x100%
Depending on the field of activity of the enterprise, the profit rate can range from 15 to 50%. With such values, the company has opportunities for growth, and its activities pay for themselves. If the rate of return is less than 15%, the enterprise has problems and its future is unstable, and if it is more than 100%, then you receive excess profits.
When calculating this indicator, it is necessary to carefully select the reporting period - in a number of industries, advanced funds have a turnover of more than one year, therefore, calculating the rate of return in a shorter period of time can lead to false results.
Analysis of the results obtained
There are three main ways to analyze the net profit received, on the basis of which you can plan changes in the operation of the enterprise in the future:
- Vertical and horizontal analysis of indicators– tracking changes in indicators and items of financial statements over a certain time.
- Trending– comparison of the dynamics of changes in profit and other indicators in the reporting period with the previous or base one.
- Factor analysis– search and consideration of external and internal factors that could affect the amount of profit received. Factors must be presented in the form of coefficients. Using all the above information, you will be able to evaluate the performance of your company and plan its further growth.
Using all the above information, you will be able to evaluate the performance of your company and plan its further growth.
Running a business is a diverse process that includes elements of management, salesperson, logistician and, of course, economist-accountant. The last aspect is ignored by most small businessmen and in vain. At its core, economic planning, and ultimately accounting, allows you not only to state the facts of profitability or unprofitability, but to suggest how to earn more money!
To clarify, let's look at economics from a real-world application perspective.
Why is it important to calculate profits correctly?
There are several basic economic indicators that realistically evaluate the activities of a business: profit, profitability, cost, revenue, income. When using the term profit, ordinary citizens mean “how much they earned”; such a definition is not entirely correct. Try asking an economist or accountant to calculate your profit?
You will receive a lot of additional questions, or they may send you to hell. In practice, such a term as profit (actually, revenue, income) are grouping definitions that denote a whole “bouquet” of different economic indicators formed at different stages of the business process.
The key definition is at different stages and processes.
What does it mean?
Profit can be calculated as the overall result of business activity; it will be net profit. In this context, we get how much money was earned (revenue minus total cost), that is, all invested funds were returned.
The simplest formula for determining net profit for business it looks like this:

This approach does not give anything, you can not count, but just move on with your life. Another thing is to calculate profit in accordance with the generally accepted mechanism, which involves determining the level of profitability, profitability of each of the stages and elements of the business.
Why is this important?
This option makes it possible to identify bottlenecks in business processes and makes it possible to work out certain measures to increase overall profitability through optimization. It doesn’t matter how much money you earn; it may well be that using everything you can earn two to three times more. The question remains, how to do this correctly?
What is profit, types
Having determined that profit (by the way, several terms are used in English - profit, gain, return) is a positive amount of money calculated as the difference between total business expenses (including cost) and total business income, revenue (sales price).
There are a dozen different interpretations, for example - Profit is the excess of all company income over its expenses or is the final financial result of the organization’s activities for a certain period of time.
There are several dozen different indicators characterizing the profitability of an enterprise; for a small entrepreneur such diversity is unnecessary; for assessment it is realistic to use several basic ones.
The main types of profit for small businesses are
- - gross
- - from sales
- - marginal
- - balance sheet
- - clean
Economic theory identifies the following types of profit:
- economic;
- accounting;
- from implementation;
- marginal;
- gross;
- balance;
- clean;
- profit (loss) before tax;
- profit (loss) from ordinary activities;
- operating room;
- nominal;
- real;
- minimal;
- normal (satisfactory);
- maximum;
- target;
- underreceived;
- cash flow;
- entrepreneurial;
- acceptable;
- undistributed (cumulative);
- taxable, non-taxable;
- consolidated;
- remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
Each of the above indicators allows you to assess the profitability or unprofitability of individual business processes, identifying those bottlenecks and allowing you to earn more. How is each indicator calculated?
Gross profit
The general characteristics of a business are carried out on the basis of gross profitability, total revenue (price of goods per quantity) (Pval), that is, an indicator showing whether the business structure functions effectively at all.

Gross profit is the difference between all revenue received and the actual cost of products sold or services provided.
Among the main factors influencing gross profitability are:
1. Internal business factors (depending on the entrepreneur or manager)
- - speed of turnover of goods (how long financial resources are frozen in balances);
- - cost of products and services;
- - marketing promotion;
- - amount of revenue (more details here);
- - quality of service (retention of regular customers);
- - unit price;
2. External factors for business (independent of the entrepreneur)
- - tax, non-tax regulation of business processes by the state (licensing, tax increases, quotas and other equivalent restrictions);
- - growth or decline in the purchasing power of the population;
- - changes in trends, fashion.
- - compensation, benefits to other manufacturers and entrepreneurs by the state;
- - political changes.
- - increased competition, changes in the price of raw materials.
After the gross profit of the business has been calculated, we move on to calculating profit from sales, but the calculation of sales profit is an interesting topic, we will put it in the framework of a separate article, you can read it here.
Now a little video about the differences between gross profit and gross income
PROFIT and Gross Income What is the difference?
Gross Income, Gross Revenue and Profit, what do they have in common?
Upload date: 2013-01-13
Marginal profit
Interesting for small businesses are calculations of marginal profit, defined as the difference between revenue (product price per quantity) and variable costs. In the article on cost, they said that costs can be fixed or variable. Variables include those parts that are directly involved in the main production process. Example:
Net profit
The final stage is the calculation of net profit from business activities, as you might guess, this is all income minus all expenses.
Let's look at several formulas for calculating profit in different interpretations

Conclusions
Such long (possibly) tedious calculations of profit at different stages of business activity make it possible to:
- finding bottlenecks to attract borrowed funds and increase profits, determining an adequate price. For example, an increase in the turnover of goods due to the expansion of the product range, assortment, and improvement of logistics;
- determine the highest priority areas of business where profitability is highest in the price of goods;
- searching for effective ways to use capital investments to increase the profitability of the entire production;
- setting threshold values for the minimum profit received at each stage;
- refusal of individual cycles, goods, services or their transfer to outsourcing, it is not for nothing that these services were included in the top most promising for 2015-2016 for small businesses.
In international finance, slightly different types of this indicator are used - EBIT (earnings before taxes and interest) and EBITDA (earnings excluding depreciation, taxes and interest). Why?
Everyone perfectly understands the desire of entrepreneurs to evade paying income taxes and, as a result, to inflate a number of indicators. This is usually done through interest on loans (lending by friendly structures), depreciation, and so on. Therefore, for a more or less real assessment of the efficiency of such a business, EBIT and EBITDA are used, that is, it is cleared only of real expenses.
Marginal profit Break-even point Operating leverage